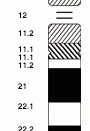
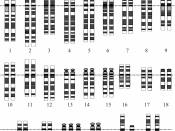
Down Syndrome, a chromosome abnormality is present in all ethnicity, social economic classes, and gender which is defined as a "congenital disorder by an extra chromosome on the chromosome 21 pair." Although there are many theories that have been developed for the cause of chromosome abnormalities, it is still not known what actually causes Down syndrome.
Down syndrome was discovered and named after a British physician called John Langdon Haydon Down who first studied it in 1866. At first it was called Mongolism because Down syndrome people have some physical features that look like Mongolian.
The affected individuals have upward slanting eyes, a fold of skin that starts at the inner corner of each eye. A deep crease across the sole of each palm and foot, one instead of two horizontal furrows on their fifth fingers, slightly flattened facial features. Their noses tend to be small, the ears are often small and the upper part of the ear may fold over.
They also have short wide necks and hands with shorter fingers. Some Down babies feet appear to have a wide gap between the first and second toe. The affected person is usually small, 145-160 cm for adults. Birth weight is usually 10-20 % below normal. Mental retardation (100 %) becomes evident at the end of first year of life. The intelligence quotient in adults is most often below 50, although some are believed to have moderate intelligence with normal IQ. Usually, the child is happy, affable, and affectionate; though walking; speech and toilet training delayed until 2 to 3 years of age. They may have delayed puberty and early menopause. However the affected women can still have children but mostly the men cannot.
In Human development, our cells normally have 46 chromosomes and divide in two ways. The first...