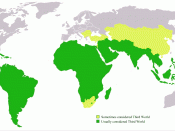
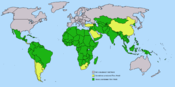
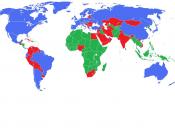
Economic Structures in the third world:
1)-A common way of defining a Third World country is by using economic criteria. Describe what the economic structures most commonly look like for a majority of Third World countries concerning production, infrastructure and foreign trade and what reasons may be for this situation.
"Third World" was first used as a political term to describe countries that were not part of the second world, communist countries of the east or the first world, capitalist countries of Western Europe and North America. The "third world" represented the newly independent countries hat were de-colonized and intending to begin a neutral position within foreign policy. Soon these countries broadened their vision to include economic attributes.
PRODUCTION:
Production in the third world is very limited to primary commodities and most countries do not compete in the industrial or manufacturing sectors. Most third world countries saw industrialization as the key element in leading them to prosperity and development.
Two positions were taken on creating industrialization; state ownership of industry and state protection of privately owned domestic industry from international competition. Most countries alternatively choose to have a specialization in trade to compete within the international economy. These countries then began to specialize in and exporting primary commodities and supposedly using their comparative advantage to gain economic stability. The comparative advantages were supposed to be capital- intense and then stimulate the economy.
These tactics did not work towards the countries advantage. They did take use of their comparative advantage to try and boost their economy but many third world countries choose the same product, creating a weak market for the products. It also made the country dependent upon their single product (ex. Guatemala-banana, UNFCO). Most countries however never reached industrialization or the production of manufactured goods. This main essential step...