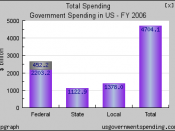
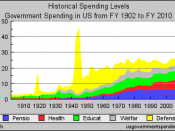
Japan has been in a recession for quite some time and has failed to recover. Price deflation, a high public debt, a loss of political leadership, and a weak U.S. economy not taking in exports, Japan's economy looks to be in trouble.
The success of Japan's economy in past years can be contributed to two parts. One part was government's active role in economic policy. The second part was the Japanese management system, which emphasized continuous improvement of cost and quality through flexible manufacturing and reduced time to market.
In reality, Japan's activist government policy explains a lot about Japan's failures, than it does about its success. Government had a marginal influence in most of Japan's most successful exports. They include such products as cars, robotics, cameras and video games. In the areas that had a lot of government regulation, it was uncompetitive, such as chemicals, aircraft, software and financial services.
The cost of living for Japanese consumers and the cost of doing business grew rapidly because of government intervention. Many Japanese companies moved offshore in the 1980s and 1990s to escape these high costs. Most of the companies could thrive if left alone. The main problem was all the government interference.
On the corporate side, Japan excelled at doing the same thing as rivals but doing it better - leading to success in many industries in the 1970s and well into the 1980s. But even in their heyday, Japanese companies were less profitable than Western competitors. By the mid to late 1980s, Western companies began to close the productivity gap by adopting Japanese practices. Then they surged ahead.
Why have reforms failed? The reforms failed because they were targeted at the wrong problem. Japan thought massive government spending would pump up domestic demand and bail out companies. Structural reforms...