1 Introduction to BS15000 IT service management standards.
BS15000 service management standards define the best practices for any organisation in implementing, delivering and managing IT services. Based on ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) BS15000 provide series of defined processes within IT services.
BS15000 is according to www.bs15000.org.uk, the world's first standard for IT service management. BS15000 is mentioned to be a formal specification defining what organisations need to achieve. The range of IT service processes BS15000 provide are as follows:
1.1 Configuration Management
Mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk configuration management is the implementation of a database. The database can contain elements of an organisation's details used in the management of the IT services. It will contain relevant information that can relate to the maintenance as well as the movement and any problems that may arise with configuration items.
A wider range of information is also held in the configuration management database that IT services of organisations rely on.
This information includes hardware, software, documentation, and personnel. Configuration management consist of 4 tasks that include identification, control, status, and verification.
1.2 Problem Management
Problem management is a process that prevents any incidents that can effect the operation of an organisation's IT services. Problem management makes sure faults are corrected and ensures these faults do not occur again.
1.3 Change Management
Change management, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk ensures all changes to configuration items are carried out in an authorised manner as well as being highly planned.
Change management makes sure that any change has business reasoning behind it and it can identify specific configuration items and IT services that are affected by any change. Planning and testing the change is part of change management as well as having a plan if change results in any unexpected state.
1.4 Incident Management/Help Desk
Help desk is the first point of contact available to business users in their IT services when problems occur. Incident control and communications are the main focuses of the help desk according to www.bs15000.org.uk. There are many different types of help desks. The type of help desk required by an organisation depends on the business requirements.
1.5 Software Control and Distribution - Release Management
Software control and distribution covers the management of software development as well as installation and support of an organisation's software products, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk.
The creation of a definitive software library (DSL) is the recommended step in software control and distribution process. Here the master copies of all software can be stored as well as being controlled and the release of software being managed. The DSL can consist of being a physical or logical store. Physical store can be software provided from external sources where master copies of software media are stored. Logical store is the releases of software, the index of them and versions.
1.6 Service Level Management
Service level management (SLM) ensures that any agreed services are delivered as and when they are supposed to be. The manager of service level can be dependant upon all other areas of service delivery, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org, providing any support ensuring the agreed services are efficient, secure and delivered in a cost effective way.
1.7 Capacity Management
Capacity management ensures that IT infrastructure is provided in the correct volume, time and price. This would help to ensure that IT is used in an efficient way. Capacity management involves input from different areas of a business to find out what services are actually required, the IT infrastructure required to help these services, the cost of the infrastructure and the level of contingency that will be needed.
Mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk, there are 6 inputs into capacity management processes:
- Performance monitoring
- Workload monitoring
- Resource forecasting
- Demand forecasting
- Application sizing
- Modelling
The results of capacity management come from these processes as well as the service level management guidelines.
1.8 Contingency Management
Should any serious incidents occur, a contingency plan should be in place that would ensure that IT services can recover and continue with minimal effect. Both reactive and proactive measures are taken into consideration in contingency planning.
Contingency planning is the recovery of the IT infrastructure used to deliver IT services, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk. Five basic steps are involved in contingency planning that include being able to prioritise businesses to be recovered, performing a risk assessment, being able to evaluate options for recovery, producing the contingency plan, and finally being able to test, review and reviser the plan.
1.9 Availability Management
Availability management identifies levels of IT service availability in use with service level reviews with clients. BS15000 mention that all areas of service must be measurable as well as being defined within the service level agreement (SLA). When measuring availability the following are included in the SLA. Agreement statistic, contingency, capacity, help desk calls, availability, and costing details.
1.10 Financial Management
Cost management ensures IT infrastructure is remained at the effective price. It calculates the cost of providing IT services so that organisations can understand it. The costs can be recovered from the customer who provides the service.
Costs, mentioned by BS15000, are divided into equipment, organisation, accommodation, software, transfer.
1.11 How companies might obtain BS15000 certification
Companies may purchase BS15000 certification from the website of BS15000 (www.bs15000.org.uk) where manuals can be purchased on the processes outlined in the above sections that will help them to improve their IT service management. Companies will need to adapt to these changes in their businesses to meet the required standards of BS15000.
The BS15000 service management standard can also be instantly downloaded and purchased by companies from the website. Manuals to purchase include BS15000-1 which is the specification to service management, and BS15000-2 which outlines the code of practice for service management, as mentioned by the office of government commerce.
1.12 Advantages and disadvantages of BS15000
The advantages of BS15000, best practice would be that it can improve customer satisfaction, increase return on your IT investment, improve staff morale and reduce staff turnover, as mentioned by www.itsmf.com.
Companies can measure themselves against which IT service they provide and demonstrate to stakeholders against the industry standards set. BS15000 is a tried and tested standard that has the advantage of being built on existing standards.
IT service delivery is widely perceived as a problem in most organisations, so BS15000 would be appreciative of. There is also no competing standards so that, just consulting firms that cannot provide the certificates that come with the industry standard.
BS15000 is a standard based on self assessment workbooks that currently has no corporate certification program.
2.0 Organisation overview
Wincanton Logistics is a leading provider of complete supply chain solutions providing outsourced logistics services in the UK as well as European markets, as mentioned on the company website www.wincanton.co.uk. The company designs and implements a range of supply chain management services based on long term contracts for their customers.
The services provided by Wincanton Logistics include:
- Supply chain systems
- Automated warehousing services
- General warehousing services
- Fleet management services
These services are offered to customers who may be in a range of market sectors including retail, high tech packaging, automotive, in-flight services, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, and industrials.
Wincanton Logistics has 360 locations across Europe with around 24,000 employees, 5,200 motive units all in 15 different European countries. Wincanton has over 100 regional distribution facilities
Wincanton Logistics is an independent business operating in its chosen markets as an integrated supply chain partner. The company's growth is organic and through acquisition of long term contracts from its customers.
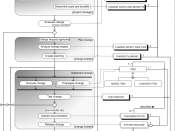
As Wincanton is based across Europe, its organisation structure is very complex. Below is an organisational chart that shows how the company would divide its work in the UK. As you can see that Wincanton Operates from its main head office in Somerset, where it also holds its whole IT department. The company can then split into three ways by the way they offer various services to their customers be this retail, industrial, or transportation. Various operations run for many customers under these 3 headings, where Wincanton has management belonging to each site.
3.0 IT overview
Wincanton Logistics run its IT operations from its Head Office for all of its sites across the UK. No individual site has its own IT department where it can be maintained on an individual basis. Using a Citrix Server Farm, the IT department is able to have complete access to all IT operations across every site. With regular backups being made for each site and installation of new software being provided from one location based at head office. All hardware is controlled from head office that includes printers, scanners, etc.
Any problems that occur with IT are to be reported directly to the IT department at head office who have the responsibility to solve the problems or queries that may occur at each site. The systems manager based at each site works in close relationship with the IT department at head office and allows regular feedback on the performance of the systems at each site.
The help desk again is run from the head office that can fix small problems through using the Citrix Server Farm technology. Any major problems will involve a call out from a member of the IT department visiting the site where problems may exist.
The principal focus of Wincanton Logistics information technology is the adaptation and enhancement of software acquired under licence from third party providers, as mentioned by www.wincanton.co.uk. Wincanton outsource a section of their IT operations that include the maintainability of their warehouse management system and fleet management system. These systems that are used in all operations at every site are provided by external companies who can support the functionality of the systems. Any problems faced with these systems are dealt with calling the help desk of the providers who would support any problems or again if major problem arrange for a call out to be made to the site.
Both LAN and WAN networks are set up at each site, linking the site operation with the system of the customers to make sure stock levels are equal and delivery and output records match both site and customer. WAN networks are setup that will able every site to be in contact with head office where performance and productivity reports can be reviewed. Communication through Lotus cc mail is used by the company to send and receive mail both internally and externally of the company.
Databases that are used include warehouse management systems able you to access stock locations in warehouses, stock movement, inventory - writing stock onto system and writing off, enter new products and check for customer orders.
The IT applications that drive the business process, mentioned by www.wincanton.co.uk, include the development of warehouse management systems for running of large automated warehouses. The development and implementation of an extranet and web-based customer systems interfaces to facilitate electronic data exchange with customers. Implementation of a web-based platform that gives customers access to real time information on order status, pallet tracking and invoicing. Implementation of a web-based platform that enables customers to access real time information on stock status within the warehouse and finally a selection of an internal e-procedure system and exploration of the potential for web-based logistics exchanges.
Mentioned already applications and information are delivered internally and externally on Wincanton Logistics infrastructure and dedicated local infrastructures.
4.0 Six selected processes
The six selected IT processes chosen for evaluation with Wincanton Logistics are:
- Configuration management
- Change management
- Contingency management
- Service level management
- Incident management
- Release management
Configuration management is chosen as a process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as the company does not have a structured register at each of its sites where components of PC's are recorded when maintenance is carried out.
Change management is chosen as another process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as changes are made to configuration items, testing the changes is carried out in an ad-hoc manner and needs to be well planned in case of the change resulting in a unexpected manner.
Contingency management is chosen as another process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as the company do not evaluate the options they have for recovery when mapping out a contingency plan for all their IT services they provide.
Service level management is chosen as another process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as problems have occurred with the company when they cannot meet the expected agreed times for services to be delivered to customers.
Incident management is chosen as another process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as help desk causes problems being situated at head office and resulting in many unanswered calls.
Release management is chosen as the final process of particular importance for Wincanton Logistics as software is not effectively controlled due to several versions of the same software around various sites across the company and not kept at the head office where the IT department is run.
5.0 IT service process evaluation tables
5.1 Configuration management
Mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk configuration management is the implementation of a database. The database can contain elements of an organisation's details used in the management of the IT services. It will contain relevant information that can relate to the maintenance as well as the movement and any problems that may arise with configuration items.
A wider range of information is also held in the configuration management database that IT services of organisations rely on. This information includes hardware, software, documentation, and personnel. Configuration management consist of 4 tasks that include identification, control, status, and verification.
The important factors to be considered are the database attributes of key network components of Wincanton Logistics. The type of information that will be held in the database will be an important factor taking the 4 tasks of configuration management into account.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Identification
Organisational BS15000 mentions that best practice involves being able to identify all IT components in the organisation that will be included in the CMDB, producing a register that will show information on each component along with its history. At Wincanton Logistics the identification becomes overlooked with the number of sites the company has in total. When new components are introduced, documentation of these components is missed out that shows relevant information on the problems that have been experienced with that component. The change that is required is the ability to recognise and record the components straight away into the CMDB that will allow identification of components where maintenance, movement, and problems can be recorded.
Control
Managerial BS15000 states that management should specify the people authorised to change each configuration item so that records can be maintained and history of each component would be well kept with the people who have been authorised. Within the company, at present, anyone working in IT support has authority to make changes to each configuration item. This has led to the registers being difficult to understand where people have not been recording enough details of the history of the components, especially with the amount of IT components based around each site. IT management dedicated to particular sites need to give authority to particular members of their team to make changes to configuration items, where it is clear who is in charge of which items at particular sites. This makes the changes be more standard with clear and regular updates to the CMDB by the same people who have authority.
Status
Organisational BS15000 looks to have a clear process to record the status of all configuration Items in the CMDB and then have this information be well maintained. At Wincanton Logistics there does not seem to be a clear process to record the status of all configuration items. It is merely done as and when there is time available by the IT department due to the size of the company. No standard procedure is followed, although when the configuration items are recorded, they are well maintained by information being entered into a database. Regular and clear processes need to be created by the company that would enable to record each configuration item, may this be hardware, software, or documentation. Recording the status of each component as and when time is available is not good enough and this will result in inaccurate and not up to date of each configuration item.
Verification
Technical BS15000 clearly mentions that reviews and audits take place to ensure that information that would be held in the CMDB is accurate and up to date. As already mentioned that regular reviews are not carried out by the company to make sure that the information they hold in their database on each configuration item is accurate. Management need to locate certain employees to make sure that regular reviews are carried out that will make sure the CMDB is accurate by going through all the information on each component that is held in the CMDB.
5.2 Change management
Change management, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk ensures all changes to configuration items are carried out in an authorised manner as well as being highly planned.
Change management makes sure that any change has business reasoning behind it and it can identify specific configuration items and IT services that are affected by any change. Planning and testing the change is part of change management as well as having a plan if change results in any unexpected state.
The important factors to be considered include making sure that Wincanton Logistic have planned any changes to be made in the control of their IT components and they have made regular testing to the changes they have carried out. In case the changes cause an unexpected action to take place, then a back up plan is needed to be implemented along with security issues needed to be taken into consideration.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Changes being highly planned -taking size of company into consideration*
Technical BS15000 states that changes should be of a highly planned nature and be in a well authorised manner Changes do not meet business requirements as they are not well planned due to the size and location of the whole company with IT being based at one single location. When carrying out any change, they need to be well planned for by taking the bottom three factors into consideration. Changes need to be made to make sure that there is a business reason behind the change.
Testing changes made*
Technical BS15000 recommends that the after making changes to the configuration items, they should be tested to make sure they are running in the way they were intended to run. After making changes, testing is not carried out on simple and small changes due to time constraints on the IT team. The company needs to make sure testing is carried out on all changes regardless of complexity of change on the configuration items. This would ensure that the IT service is being provided at a high level.
Back up plan for changes being carried out.
Managerial BS15000 mention that a back-up plan should be created if the changes that are carried out do not go accordingly to plan. Wincanton do not create back up plans if any changes to the configuration items go wrong and records of previous changes are not kept in a structured format. The company need to create a plan before any changes are carried out that would show them what to do if the changes they have made are not correct.
Taking IT security into account with changes*
Organisational BS15000 states the importance of IT security that need to be taken into consideration to make sure all changes have been taken into consideration for risk and how the changes might cause an impact on the business. Wincanton do not take Security serious enough that make their change management procedures be effective. As authorisation is given to all people in the IT team to make changes, major impacts could be made on the company like financial loss. Firstly as already mentioned authorisation needs to be provided to certain people in the company to carry out changes to configuration items. Secondly all changes that are made need to be assessed for risks by taking into account how it would cause an impact on the company.
5.3 Contingency management
Should any serious incidents occur, a contingency plan should be in place that would ensure that IT services can recover and continue with minimal effect. Both reactive and proactive measures are taken into consideration in contingency planning.
Contingency planning is the recovery of the IT infrastructure used to deliver IT services, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk. Five basic steps are involved in contingency planning that include being able to prioritise businesses to be recovered, performing a risk assessment, being able to evaluate options for recovery, producing the contingency plan, and finally being able to test, review and reviser the plan.
The important factors that need to be considered include the various measures that organisations can take into consideration and then the ways of being able to produce a risk assessment that will show you the risk on each disaster, ways to evaluate the options for being able to recover from a disaster happening, and able to maintain the contingency plan to make sure the plan remains up to date.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Types of measures to take into consideration*
Organisational BS15000 recommends that not only reactive measures should be taken into consideration by organisations, but also proactive to stop something occurring in the first time. Wincanton produce a contingency plan that only covers reactive measures on ways to solve any problem should it arise that would affect the IT service they provide. It would be recommended for the company to produce a proactive plan as well, that would help them to distinguish problems that would prevent an unexpected situation occurring first time round.
Performing a risk assessment
Organisational BS15000 suggests carrying a performance risk assessment for every IT service organisations provide to identify assets, threats, and vulnerabilities for each service. No performance risk is carried out on any service provided by the company. The threats and vulnerabilities are not shown in the contingency plan of each service. The potential impact of each disaster should be considered by Wincanton and then a risk assessment should be carried out that shows countermeasures for each service.
Evaluating options for recovery
Organisational BS15000 states that the contingency plan should contain areas where you are able to evaluate the options for recovery in order to know how successful the options would be in case of a disaster occurring. Options are created by Wincanton although little emphasis is taken consideration into the evaluation phase for the options. Wincanton need to make sure that every option they create that they need to deploy a full evaluation phase for it in order to know how useful the option would be if a problem occurred as well as how quickly the option would solve the problem.
Maintenance and testing
Organisational/
technical BS15000 emphasis on the importance of being able to maintain and test the plan to make sure it remains current. Regular reviews and testing is not carried out by the company. Once the contingency plan is drawn up, it is left till any problems occur and then reviewed. Wincanton need to revise their contingency plan on regular basis to make sure improvements can be implemented and that each option for a problem if occurred is still valid and able to be up to date.
5.4 Service level management
Service level management (SLM) ensures that any agreed services are delivered as and when they are supposed to be. The manager of service level can be dependant upon all other areas of service delivery, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org, providing any support ensuring the agreed services are efficient, secure and delivered in a cost effective way.
The important factors to be considered include user perspective service level agreement (SLA) monitoring, and reporting capabilities, in terms of performance and availability.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Producing contracts on agreement*
Managerial BS15000 mentions SLA be an essential part for the provision of service to make sure agreed services are delivered on time. As parts of the IT used by Wincanton are outsourced, clear contractual agreements between both parties are not set up as efficient service is not provided and has resulted being very costly to the company. A full service level agreement needs to be produced that would outline the parameters for the delivery of the service as well as distinguish who would be to blame if a disaster takes place.
Review of 3rd party service providers*
Managerial BS15000 recommends that regular reviews to be carried out on service providers to your organisation. Wincanton have never carried out a review of providers of their warehouse and fleet management systems since first chosen to be their system providers. Regular reviews would ensure that the service provided is still met as set in the service level agreement.
Implementation of service improvement policy and processes.
Managerial BS15000 states that there should be a policy in place for service improvement, outlining the processes involved. The company does not have in place a service improvement policy that would show them ways to improve their service levels. Wincanton need to introduce a service improvement policy that would help in distinguishing ways to improve the IT service being provided to the company.
5.5 Incident management
Help desk is the first point of contact available to business users in their IT services when problems occur. Incident control and communications are the main focuses of the help desk according to www.bs15000.org.uk. There are many different types of help desks. The type of help desk required by an organisation depends on the business requirements.
The important factors to be considered include help desk and incident control and communications. The calls answered by the company as well as the quality of the service and security issues in place.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Waiting time for call to be answered*
Operational Best practice states that there should be high first call resolution and low call abandonment rates as well as fast answering of calls. Help desk only operates during office hours, which is not beneficial as the company operate on a 24 hour basis. When calls are made it takes approx 5 minutes to get through to speak to help desk staff. Longer hours of operating the help desk is required by Wincanton, with the possibility of more staff being employed due to the length of queues employees have to wait in to get their incident reported.
Quality of help desk software*
Operational Best practice would involve the software having good GUI and where users do not have to flick between modules to update changes. Allow alerts to be received for the generated incident. Options given by the current software are not currently working according to the problems that are arising. Too many screens make it difficult to give feedback and support to employees. Fewer modules are required in the software where less time would be used and users would be able to move from screen to screen freely without having to go back or have limited options available to them.
Training*
Operational Best practice would entail all help desk staff to be well equipped with the skills they need to resolve and prevent incidents from occurring regardless of complexity of problem. Experienced staff only answer escalated calls and simple call loggings are carried out by employees with no previous training. All staff need to be trained fully to the complexity of their job. This would result in better IT service being provided to people calling for help at the help desk.
IT security*
Operational BS15000 that the help desk is the main contact when something is carried out of the ordinary. Staff can make sure recurrence of incidents and limit impact of breaches in IT security. The help desk at Wincanton does not ensure prevention of incidents of the IT services being provided. Also same faults keep occurring to be problems which need to be taken care of. Better skilled staff would prevent recurrence of incidents and employ instigate measures. Training would need to be carried out or introduce better software for help desk staff.
5.6 Release management
Software control and distribution covers the management of software development as well as installation and support of an organisation's software products, as mentioned by www.bs15000.org.uk.
The creation of a definitive software library (DSL) is the recommended step in software control and distribution process. Here the master copies of all software can be stored as well as being controlled and the release of software being managed. The DSL can consist of being a physical or logical store. Physical store can be software provided from external sources where master copies of software media are stored. Logical store is the releases of software, the index of them and versions.
The important factors to be considered include the creation of a software library, the authority of people having access to software items, and the relationship between software control and distribution and IT security.
Activity/service factor/ measurable Type M/T/O Best Practice Current organisational state Organisational change required
Creation of software library
Organisational BS15000 states that a recommended storage be created where all software is stored and controlled. No library exists within the company and several versions of the same software are kept at various sits of the company. A Definitive Software Library needs to be created where all software configuration items can be monitored by knowing their distribution across sits.
Access to software configuration items*
Managerial BS15000 mentions that the software stored in the DSL is controlled and the release of the software should be well managed. No authority is given to employees that would have control and authority of software. Copies of software can easily be copied and unlicensed versions of software can easily be produced. Management need to control the software configuration items within the company and possibility employ someone to keep access of the software of how it will be built, released and audited.
IT security*
Managerial BS15000 states that if software is managed inappropriately, then the services being provided can become unavailable if availability, confidentiality and integrity is exposed. The company do not conduct correct software modifications and in the past this has led to malicious damage to data files. Full reviews are not carried out on regular basis of the software control and distribution procedures. Better software control is required by the company that would result in the services being provided available all times. In depth reviews are needed to be carried out by the company that would also ensure that there are appropriate counter measures in place to reduce the threats. Appropriate procedures need to be produced and maintained that would enable a control on the release of software.
5.7 Sources and Notes for Process Tables
The definition of information came from experience of working in a help desk role at Wincanton Logistics where findings of IT services can be brought together to comment on the issues concerning best practice when looking at the processes of BS15000.
6.0 Summary table
In order for Wincanton to create organisational readiness the following actions in the table below need to be carried out for each process.
Action Priority Process Organisational Activity
Identify all IT components.
Produce a well maintained CMDB.
Configuration management
The company need to keep an asset register firstly of all hardware, software, documentation, and personnel across all sites within the company. Secondly a database needs to be produced that will contain all the elements of the IT services being provided by the company on maintenance, movement, and the problems of the configuration items. The CMDB will specify the authorisation of people allowed to change it, and it will allow management to regularly keep undated information on changes made to deploy accuracy.
The need to test changes when carried out.
Ensure a back-up plan is produced in case of changes cause an unexpected result.
Change management
Any changes that are made need to be tested by the company so that the change complies with the requirements of the business as well as the reason for the change on the configuration item. This will ensure that any unexpected result will not cause an affect on the IT service being provided. As well as this, the company needs to ensure that a plan is produced in case of any problems that may occur as a result to the changes. This again would limit the damage on the IT service by being well prepared for any unexpected change.
The need to produce a risk assessment so that the company knows the types of risks that can arise and their threats to the company.
The need to know how constructive the options that are produced would be in case of an unexpected threat.
Contingency management
A risk assessment needs to be produced by the company that would show them the various consequences of each risk to the IT services it provides. This would show the company the threats of each risk so that if the risk does occur, the company would be well prepared by summarising its potential impact to the company's IT services. Each risk would as mentioned need to be evaluated to show the danger of its performance on the operation of the company.
The need to review the contract held with current 3rd party IT service provider in order to make sure the IT service is still being provided to the standard originally stated.
The need for Wincanton to produce a service improvement policy.
Service level management
Wincanton need to review their contract that is set up with the providers of their warehouse and fleet management systems to ensure that the IT services standards are still met. Problems are occurring that indicate they are not being met, so a full review will able the company to find out the level of service being provided to them. This will allow the set up of a service improvement policy that would outline the processes for all parties involved on ways to improve IT service standards.
The need for better quality help desk software
The need to introduce longer hours of help desk service being provided to all sites.
Incident management
The implementation of better help desk software is required where employees have easier scripts to follow that would allow active responses to people's problems. Fewer modules would be needed and more options for people's queries would be required. The help desk does not operate long hours as already mentioned, so perhaps more people need to be recruited to work on the help desk where there is always cover while the company runs its operation.
The need to produce a Definitive Software Library for the control and release of the software.
The need for management to give authority to have control of the library where unauthorised modifications can be carried out.
Release management
A library would be needed to be created that would enable the control of the software that is currently being released to all sites without the correct authorisation procedures. This would give the control of unauthorised modifications of the software and would prevent any threats taking place. Authority needs to be controlled on the access of the library where software can be released.

Nice piece of work
Seriously this is a well described and in depth essay, very well written and explained. Good work.
1 out of 2 people found this comment useful.