Name 1
NAME
UNIVERSITY
Ancient Peoples of the World
PROFESSOR
Is There Neanderthal in Us?
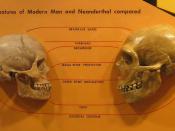
Over the course of human history, an abundant amount of information has been found on the evolution of our species, Homo sapiens. Of those, Neanderthals are a species whose origin has been debated and interpreted in different views. They are an extinct hominid lineage and their role in the evolutionary history of modern humans is a well concern topic (Wang and Farina 2013). One prominent view is that Neanderthals are in fact human, Homo sapiens and are a sub species. The contrary view is that Neanderthals are a complete separate species, Homo neanderthalensis, and humans replaced their population (Wang and Farina 2013). Because both these views are on complete opposite sides of the spectrum, it is very easy to distinguish between the two. Their prominence is important because as humans, having concrete information on our evolution in itself is very important to our future development.
That being said, Neanderthals are seen as that link between our beginnings and the modern humans we see today. Ultimately, the resolution of this debate will yield much better focus on putting together the big picture of how modern humans came about and by what means.
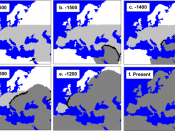
Roughly 300,000 years ago, the Old World was occupied by a morphologically diverse group of hominids. In North America, Africa and the Middle East there were Homo sapiens; in Asia, Homo erectus; and in Europe, Homo neanderthalensis (Trinkaus and Shipman 1992). By 130,000 years ago, Neanderthals had all become so anatomically distinct that they were classified as a separate species, Homo neanderthalensis. Over time, they became extinct and to date, no definite Neanderthal specimens newer than 25,000 years ago have ever been found (Lewis 2010). In 1999, a...