Study Guide"ÃÂMendel and Meiosis (+ some mitosis) 1. Be able to do a monohybrid cross.
Example: Hh x hh 2. Know heterozygous vs. homozygous 3. Know difference between genotype and phenotype.
4. Know difference between dominant and recessive.
5. Be able to do a dihybrid cross.
Example: H = hairy face, h = non-hairy T = no teeth, t = teeth What is the genotype of a man who is heterozygous for a hairy face and has teeth? (answer: Hhtt) What are all the possible allele combinations he can pass on through his gametes? (answer: Ht, Ht, ht, ht) 6. Know all about Mendel's experiments.
Started with true-breeding parental generation ; crossed 2 of these plants with different traits.
F1 generation = offspring; all had the same trait = dominant Self-pollinated F1 generationÃÂýoffspring = F2 generation; For every 3 plants that had the dominant trait, there was 1 with the "recessive" trait.
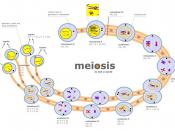
7. Why were pea plants a good choice to use? 8. Know/apply Mendel's Laws (dominance, segretation, independent assortment) 9. Meiosis (vs. mitosis): occurs in gametes (sex cells); makes haploid cells (only 23 chromosomes); Two cell division stages make 4 daughter cells, homologues pair up, etc.
Look at meiosis pictures. Know what's going on in each phase.
10. What are Homologous pairs? What is crossing over? Why is it important for genetic variation? 11. What is haploid vs. diploid? 12. What is the cause of cancer? What are some risk factors? 13. What are some mistakes that may occur in meiosis and characteristics that result? (nondisjunction"ÃÂDown Syndrome (= trisomy 21), Turner's Syndrome (= XO)