Outline
- Introduction
- Types of lipids
- Structure of lipids
- Functions of lipids
- Test for lipids
I. INTRODUCTION
- Lipids are a loosely defined group of molecules with one main characteristic: they are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents (e.g. chloroform).
- Lipids consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen - but much less oxygen compared to hydrogen.
- No generalized formula
- Difference between a fat and an oil:
- If a lipid is in the solid state at 20oC, it is a fat.
- If it is in the lipid state at 20oC, it is an oil.
II. TYPES OF LIPIDS
1. Simple lipids
- Esters of fatty acids with various alcohol.
- Fats - esters of fatty acids with glycerol (e.g. triglyceride)
- Waxes - esters of fatty acids with complex alcohol.
2. Compound lipids
- Lipid + non-lipid components.
- E.g.
Phospholipids = lipids made up of fatty acids + alcohol (e.g.glycerol)
+ phosphate
III. STRUCTURE OF LIPIDS
ô Components of lipids : fatty acids + glycerol
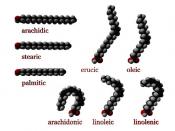
- A fatty acid consists of : a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group.
- A hydrogencarbon chain consists of : a chain of carbon atoms to which hydrogen atoms are attached (vary in length, but most common are even numbered chains of 14 to 20 carbons).
- Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, each bearing a hydroxyl group.
ô Synthesis of a triglyceride
- Three fatty acid molecules + one molecule of glycerol.
1
IV. FUNCTIONS OF LIPIDS
1. Triglycerides is a storage form of energy.
2. Good thermal insulator - to prevent excessive heat lost
3. To protect delicate organs
4. As a component of cell membrane
V. TEST FOR LIPIDS
ô Principle:
- Lipids are readily soluble in...