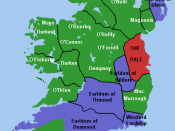
Catastrophic Dimensions This essay's intent is to assess the relationship between the anti-Catholic legislation passed by the Irish parliament of 1613-1615 and the emergence of a distinct national identity in early modern Ireland. For almost four centuries, the royal administration in Ireland had distinguished between the Gaelic Irish populations in the hinterlands of Leinster, Munster, Connacht, and Ulster, and the English population in the Pale, that relatively urbanized settlement centered on Dublin, and in the outlying towns and earldoms of Leinster and Munster. The parliament of 1613-1615 gave legal force to a new, equally impermeable cleavage between the two components of the Anglo-Irish(1) colonial community: the Old and New English. The New English were recent Protestant transplants, sent from England by the crown during the sixteenth century to operate the Irish government. The Catholic Old English were natives of Ireland. Descendants of the original twelfth-century Anglo-Norman conquerors, the Old English shared an Anglo-Irish heritage and the common interests shaped by that heritage.(2)
By securing the rigorous enforcement of the Oath of Supremacy, the implementation of revenue-generating recusancy fines, the expulsion of all Jesuits and seminary priests from Ireland, and the confiscation of Catholic lands during the parliament of 1613-1615, the New English government systematically excluded the Catholic Old English from political and social influence on the grounds of religion.(3) The interpretation of the Irish government's shift from racial to religious discrimination raises profound historiographical questions, for the attempt to locate this shift in a framework of cause and effect requires the historian to confront the problematic concept of Irish nationalism. This task has provoked significant debate among historians of early modern Ireland.
![Catholic Immigration Map of Western Canada [1900]](https://s.writework.com/uploads/6/68304/catholic-immigration-map-western-canada-1900-thumb.jpg)