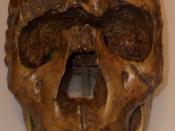
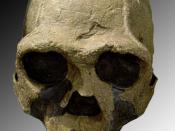
A new lineage of the genus Homo emerged in Africa around 1.9 million years ago known as Homo ergaster. Homo ergaster, which is translated as workman, is thought to be an early version of Homo erectus. Homo ergaster is a species name used to indicate the fossils of Homo erectus, Homo heidelbergensis, and Homo sapiens that lived in Africa during the Lower Pliocene. An almost completely intact Homo ergaster skeleton, called the Nariokotome boy, was discovered in August of 1984 by a scientific team led by Richard Leakey on the west bank of Lake Turkana, Kenya. Nariokotome boy gives us the best description of this species, because before its discovery, there were only two skulls that defined this entire species.
The Nariokotome boy, after analysis, was revealed to be an 11-12 year old boy that died from septicemia after the shedding of one of his milk teeth.
In today's time, antibiotics would have protected us from such an infection; however Nariokotome boy perished falling face down in the marsh and was buried by swamp mud for 1.5 million years. Nariokotome boy is estimated to have been about 5 ft. 3 in. tall at death, which is unusual for an 11 year old and it is thought that he have reached 6 ft. 1 in. tall if he would have lived into adulthood. He was tall, muscular and had a sturdy skeleton. He was about 78 lbs. at death and would have probably reached 154 lbs. One of the most surprising things about the skeleton was how closely it resembled modern humans living in conditions similar to that of Nariokotome boy. The limb proportions are very much that of modern humans except for the shin bones, which are longer than ours and the lower limb...