The International Space Station draws upon the resources and the scientific and technological expertise of 16 cooperating nations, including the United States, Canada, Japan, Russia and 11 participating member nations of the European Space Agency -- Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. In addition, Brazil and Italy have signed on as payload participants.
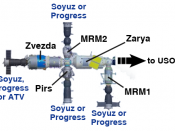
The living and working housing will be the equal to the passenger and load capabilities of a jumbo 747-400.Along with the environment module there will be 7 laboratories - 3 Russian, 2 American, One European and 1 Japanese The current modules that are in space are Zarya, Zvezda, Unity & Destiny modules, the next to turn up is the US Airlock system.
Right now the International Space Station is not complete, it will have a mass of almost one million pounds, be larger than a five-bedroom house and measure 361 feet end to end.
Four American photovoltaic modules will provide power to the space station, each with two arrays measuring 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. Each module generates about 23 kW. The total surface area of the arrays will be more than half an acre! This electricity is distributed through the station via 8 miles or almost 13 kilometers of wire. The space Station uses 45 kW just for research, experiments. The ISS use a 110 kW of electricity this is equivalent to ten houses using electricity.
Fifty-two computers will control the systems on the International Space Station. The flight support software has 1.7 million lines of code. The 58-foot robot arm CanadArm2, can lift payloads of up to 220,000 pounds.
The international Space station orbits at a standard altitude of 220 miles at a slant of 51.6 degrees to the equator. The...


Essay
that was a good essay on the space station it got me a 103. A+ job thanks
0 out of 0 people found this comment useful.