Economic surplus: the benefit of taking an action minus its costs.
Opportunity cost: the value of the next-best alternative that must be foregone in order to undertake an activity
Sunk cost: a cost that is beyond recovery at the moment a decision must be made.
Average benefit: the total benefit of undertaking an activity divided by the units of the activity.
Average cost: the total cost of undertaking an activity divided by the units of the activity.
Marginal benefit: the extra benefit from undertaking one more unit of an activity.
Marginal cost: the extra cost from undertaking one more unit of an activity.
Absolute advantage: one person has an absolute advantage over another if he or she takes fewer hours to perform a task than the other person.
Absolute advantage: one person has an absolute advantage over another if he or she takes fewer hours to perform a task than the other person.
The Principle of Comparative Advantage: Everyone does best when each person (or each country) concentrates on the activities for which his or her opportunity cost is lowest.
Production possibilities curve: a graph that describes the maximum amount of one good that can be produced for every possible level of production of the other good.
Attainable point: any combination of goods that can be produced using currently available resources.
Unattainable point: any combination of goods that cannot be produced using currently available resources.
Inefficient point: any combination of goods for which currently available resources enable an increase in the production of one good without a reduction in the production of the other.
Efficient point: any combination of goods for which currently available resources do not allow an increase in the production of one good without a reduction in the production of the other.
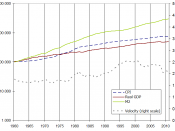
Standard of living: the...