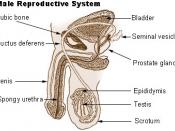
Male Reproductive System
The organs of the male reproductive system are specialized for the following functions:
To produce, maintain and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen)
To discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract
To produce and secrete male sex hormones
The male reproductive anatomy includes internal and external structures.
External Reproductive Structures
Most of the male reproductive system is located outside of the man's body. The external structures of the male reproductive system are the penis, the scrotum and the testicles.
*Penis -- The penis is the male organ for sexual intercourse. It has three parts: the root, which attaches to the wall of the abdomen; the body, or shaft; and the glans, which is the cone-shaped end of the penis. The glans, which also is called the head of the penis, is covered with a loose layer of skin called foreskin. The opening of the urethra, the tube that transports semen and urine, is at the tip of the glans penis.
The penis also contains a number of sensitive nerve endings.
Semen, which contains sperm, is expelled (ejaculated) through the end of the penis when the man reaches sexual climax (orgasm).
*Scrotum -- The scrotum is the loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. It contains the testicles (also called testes), as well as many nerves and blood vessels. The scrotum has a protective function and acts as a climate control system for the testes. For normal sperm development, the testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temperature. Special muscles in the wall of the scrotum allow it to contract and relax, moving the testicles closer to the body for warmth and protection or farther away from the body to cool the temperature.
*Testicles (testes) -- The...