Define what is meant by market equilibrium. With the aid of diagrams, explain how market forces determine equilibrium price and quantity. Discuss the reasons for and methods of government intervention in markets.
A particularly notable feature of market economies is the effect of the price mechanism on demand and supply. The price mechanism determines the equilibrium in the market and is the interplay of the forces of supply and demand in determining the prices at which commodities will be brought and sold in the market. Market Equilibrium is the situation where, at a certain price level, the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of a particular commodity are equal. This means that the market clears (there is no excess supply or demand) and there is no tendency for change in either price or quantity. Sometimes, the equilibrium quantity that results from free interplay of demand and supply may be considered too high or too low and some goods and services may not be produced in the market because it is considered unprofitable.
Governments have to intervene in the market because in practice, market economies are not entirely successful in achieving maximum satisfaction.
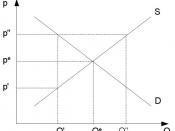
Diagrammatically, market equilibrium occurs where the demand and supply curve intersects, at the point where the quantity demanded is exactly equal to the quantity supplied. To establish market equilibrium, surplus and shortage of goods and services must be eliminated until supply and demand curves are equal. Let us first consider the case for excess demand, where the current price is below the equilibrium, as shown in Figure 1:
(diagram)
A shortage is when supply is less than demand. In this situation, buyers will begin to compete for limited goods and will raise the price. More suppliers will also enter the market at this time. A raise in price...
Comment
Regulating public transport with a price ceiling won't lead to excess supply if theres a rule that the firms also have to meet demand at the regulated price - difference between a monopoly and the supply curve of a competitive industry.
0 out of 0 people found this comment useful.