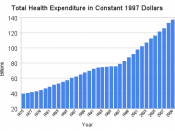
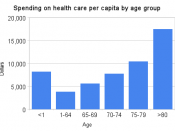
Health care and Pension plan problems are more visible every year for the Canadian population and raise concern in several institutions that may be affected by these problems. Sociologists and Economists study the economic consequences of demographics in Health Care and Pension Plans and suggest possible fiscal solutions that would help fix this problem. Nevertheless, most of the times the use of Fiscal Policy to solve Pension and Health Care problems just creates more problems because it only increases public expenditure. The most practical and efficient solution for the Health Care and Pension problems is the capitalization of these institutions making an extensive use of financial intermediation.
The problems that CPP, QPP and Health Care face have the same origins but it is necessary to make reference to how these institutions are established and then see the problems that they may incur in. This is a brief explanation of the systems.
The Canadian Pension Plan (CPP) and the Quebec Pension Plan were established in 1966 and the contribution to these funds is mandatory for every working Canadian. The amount of the contribution is a fixed percentage of the employee's earnings, to a maximum, to then be matched by the government.
As Siklos (1994) states, CPPs are invested, generally, in provincial government bonds that can not be traded in the market but the revenues of these bonds are paid out of general revenues. In the same way the QPP are invested in provincial bond, with the difference that the Caisse de Depot et Placement manages this fund like an ordinary pension fund.
On the other hand the Canadian Health care system is provided by the Federal Government in coordination with Provincial Governments. The health care system uses resources from income taxation. This way every Canadian contributes to Health Care when paying...