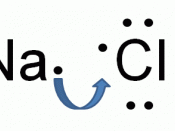C2.1: Structure and bonding
2.1.1: Chemical bonding
When two or more elements react together compounds are formed. The atoms of elements join together by sharing electrons or by transferring electrons to achieve stable electronic structures. Atoms of the noble gases have stable electronic structures.
When atoms of non-metallic elements join together by sharing electrons it is called covalent bonding.
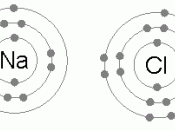
Elements in Group 1 of the periodic table have atoms with one electron in their highest occupied energy level (outer shell). Sodium atoms, Na, (electronic structure 2, 8, 1) form sodium ions, Na+ (electronic structure 2, 8).
Elements in Group 7 of the periodic table have atoms with seven electrons in their highest occupied energy level (outer shell). Chlorine atoms, Cl (2, 8, 7) form chloride ions, Cl- (2, 8, 8).
The compound sodium chloride has equal numbers of sodium ions and chloride ions so we write its formula as NaCl.
Key words: covalent bonding, ion, ionic bonding
Examples of questions likely to come up in this section:
How can you tell the compound H2O has covalent bonds?
Which of these compounds have ionic bonding? KBr, HCl, H2S, Na2O, Cl2O, MgO
Explain what happens to the atoms of the elements when lithium reactions with fluorine.
2.1.2: Ionic bonding
Ionic bonds hold oppositely charged ions together in giant structures. The giant structure of ionic compounds is very regular because the ions all pack together neatly, like marbles in a box.