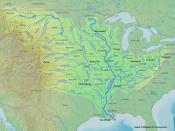
Mississippi is an Indian word, meaning "Great River" or "gathering of water".
The Mississippi River is one of the world's major rivers in size and habitat diversity.
It is the third longest and largest river in the world, the second largest in North America.
It flows 3,705 kilometers from its source at Itasca in the Minnesota North Woods, through the mid-continent United States. The Mississippi enters the Gulf of Mexico about 160km downstream from New Orleans, through a 26, 150-sq km delta.
The Mississippi River is divided into three parts: the Headwaters, the Upper Mississippi River, and the Lower Mississippi River. The average of surface speed of the Headwater of the Mississippi is near 1.2 miles per hour, as fast as people walk.
The lower river, which has a relatively narrow but deep channel, is navigable for oceangoing ships upstream to Baton Rouge.
The Mississippi River and its adjacent forests and wetlands provide important habitat for fish and wildlife.
It includes the largest continuous system of wetlands in North America. The river supports a diverse array of wetland, open-water, and floodplain habitats, including extensive habitats on national wildlife refuges. The Mississippi river and its floodplain are home to a diverse population of living things. Forty percent of the nation's migratory waterfowl use the river corridor during their spring and fall migration.
Sixty percent of all North American birds (326 species) use the river as their migratory flyaway. Many more animals use the river as their home.
The Mississippi carries an average of 436,000 tons of sediment each day. Over the course of a year, it moves an average of 9 million tons of sediment. Because of the sediments the River is threatened by a variety of pollutants. Municipal, industrial, and agricultural pollutants have been identified...