MITOSIS
Occurs in somatic cells.
Consists of only one nuclear division.
Cytokinesis takes place only once.
Involves division of chromosomes.
Dividing cells can be haploid or diploid.
Does not involve either pairing of homologous chromosomes or crossing over.
Two daughter cells are formed.
Number of chromosomes present in the mother cell is maintained in both the daughter cells. Therefore it is an equational division.
Original characters of the chromosomes are maintained in the daughter cells.
Daughter cells are similar to each other and also to the original mother cell.
Helps in growth and body repairs.
MEIOSIS
Occurs in reproductive cells.
Consists of two nuclear divisions M-I and M-II.
May take place only once (simultaneous type) or twice (successive type).
Involves separation of homologous chromosomes in M-I and division of chromosomes in M-II.
Dividing cells are diploid.
Pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over occur during Prophase-I.
Four daughter cells are formed.
Diploid number of chromosomes is reduced to haploid in each daughter cell. Therefore it is a reduction division.
Chromosomal characters are altered due to "crossing over" causing recombination of genes.
Daughter cells differ from each other as well as from the original mother cell.
Helps in the sexual reproduction and regulation of chromosome number in the life cycle of sexually reproducing organism

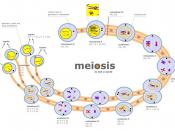
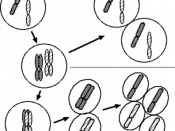
Mitosis and Meiosis
Great notes on Mitosis and Meiosis. They're very clear and to the point. A good resource to utilize. I'll definitely be using it to study from. Thanks :)
6 out of 6 people found this comment useful.