Outsourcing
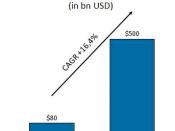
The reliance on outsourcing as a means of providing information technology (IT) services has been growing steadily over the past decade. It was recently estimated that IT outsourcing would reach US$ 156 billion in 2004 (Lacity & Willcocks, 2000). The facts that firms are increasingly turning to external suppliers in order to meet their IT needs does not mean that outsourcing is a panacea or that it is without problems. While it may help clients achieve major benefits such as cost savings, increased flexibility, higher quality services and access to new technology ( McFarlan & Nolan, activities 1995).
IT outsourcing is broadly defined as a process undertaken by an organization to contract out or sell the organization's IT assets, staff and or to a third party supplier who in exchange provides and manages IT assets and services for monetary return over an agreed period of time ( Kern et al.,2002).
In this contractual relationship the outside vendor assumes responsibility of one or more IT functions, but alternative functions may require alternative processes.
Quinn, 1992 "outsourcing gained wide spread acceptance because firms must constantly seek to lower their cost structures, respond with great flexibility to changing market conditions and market uncertainty in general"
Pros and cons of outsourcing
Outsourcing is a strategically important activity that enables an enterprise to achieve both short and long term benefits.
In outsourcing, cost benefit appears to be a compelling argument of contracting out services previously performed internally (Anderson & weitz, 1986)
Its efficient. Outsourcing provides seasonal labour without the overhead of permanent hires, which is particularly helpful to firms dealing with a staff shortage. Firms with enough people to handle busy season but that worry about a glut of unused hours the rest of the may see a benefit too.(Shamis et al., 2005).
Allows firm to handle more work. Many firms are selective about accepting new work during busy season, and most have had to turn away profitable client at times. Outsourcing arrangement can accommodate new engagements that come up in cases like this.
It usually offers lower labor costs. When firms outsource they normally do so to get lower labor rate by having the job done where the cost of labor is cheap.( Murray, 2005).
Outsourcing adds flexibility to client operations, it free up capacity and allows clients to focus on their core competencies, such as investment and relationship management.
Clients benefit from the offshore location, without having to incur the expense of setting up, or maintaining the necessary infrastructure. And clients gain from the proven track record and expertise of regulated, highly regarded offshore providers who can provide tailored solutions to their middle and back office requirements.( Henderson, 2005).
Outsourcing continues to be a popular business strategy, although companies are now gaining more experience with the realities of it, many are still battling unrealistic expectations. The cost savings and service quality they hoped for may not materialize. The reason is that outsourcing arrangements fall short of expectations and this does not really surprise human resource professionals: Lack of planning and implementation, not including vendor accountability and the lack of opportunity to measure results are key factors in a successful outsourcing.(Sandler, 2005)
The following are considered as mistakes companies make when outsourcing.
Picking the right technology ; A lot of companies don't take this into consideration. Tools are important to do a job, but they have to be the right tools-robust and scalable enough to deal with specialized and unique circumstances. Most Human Resource Management Systems were not built to support complex employee benefits administration environment and the different processes, reporting requirements and work flows associated with them. Ideally, what should be required is a technology platform certainly web-centric that is built specifically to accommodate a multi-company environment.
Confusing core and critical functions; Some companies also make the mistake of confusing core and critical functions, just because something is critical to ones business does not mean that it's a core skill or knowledge that one need to retain in house, recruit, train, support, manage or sell.
Failing to define the scope of the work; Both the boundaries and the scope of work to be outsourced must be clearly defined in the evaluation so that respective capabilities can be determined and succinctly documented. Surprises are the worst enemy of any evaluation, selection and implementation process. It is important to know exactly what one is outsourcing, the advantage of outsourcing that function, how it supports the companys strategic objectives, how it aligns with other domains and resources in the company and what the real consequences of failure could be.
Not communicating expectations; Oftentimes, despite their best initial intentions, buyers are pressed to get the deal done and they rush to initiate the implementation process as soon as possible, leaving the details to a less than informed implementation team. This mistake will almost always result in a messy and delayed implementation, one that is mired with disfunctionality, not respectful of process and certainly over budget.
Underestimating the power of change; Changes due to outsourcing very often are perceived negatively by employees, particularly those directly impacted.
They need to ensure that the professional services agreement includes some governance and much defining measurable milestones that the vendor is required to deliver and stipulates how these milestones will be monitored and measured throughout the life of the professional relationship. The milestones should be specific, measurable and reportable.
Signing an inadequate service agreement; Service agreement need to realistically acknowledge and value differentiated offerings and their associated pricing. And if there is an expectation that the environment will become highly competitive, the time frame during which this is considered likely to occur should factor into the terms of the service agreement.(Kevin & Eric 2005).
Is client information secure. With outsourcing issues of security of client data are so crucial. How this is handled and its confidentiality remains an issue that should be addressed.(Gentle, 2005).
Is it more efficient. Firms say the process is not cost efficient for returns that can be completed in one or two hours, but yields savings on those that take longer. But some say partners who manage and monitor the outsource process may find the value of their time makes outsourcing more expensive than doing the job in-house.
In the long term, blind offshoring will not only hurt companies through inefficiency but will also jeopardize their intellectual property. Culture, local laws and lack of visibility impose significant challenges in protecting intellectual property when offshoring. For example knowledge cannot be shielded, and virtue exists in sharing it.(Heidari, 2005).
Lack of control. Problems can also arise as a result of you not being able to control the firm especially in case where the outsourcing is that of offshoring.
Loss of control, declining rate of innovation, low performance, high transaction costs, other hidden cost including loss of key IT employees and dissipation of competitively relevant knowledge, including loss of absorptive capacity to monitor technological advance as well as motivation loss of remaining employees are all risk associated with IT outsourcing.