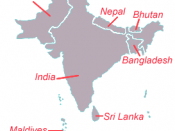
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), comprising the seven South Asian countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka, formally came into existence in 1985 with the adoption of its Charter at the first Summit in Dhaka (7- 8 December 1985). The idea of regional cooperation was first proposed through 'a regional forum' by Bangladesh in 1980, with a view to holding periodic, regional-level consultations among countries in South Asia on matters of mutual interest and possible cooperation in economic, social, cultural and other fields. The rationale was primarily predicated on the premise that regional experiences elsewhere in the globe had been highly successful and that the countries in the South Asian region would benefit enormously from such cooperation as it would strengthen their competitive position, both individually and as a group as compared to the other global communities like the EU.
The Bangladesh proposal argued that inherent logic strongly justified regional cooperation, particularly among South Asian countries, because the countries in the region enjoy geographical contiguity, historical, social, cultural and ethnic affinities which would act as centripetal forces and thus, contribute significantly to facilitate coordination and to reduction of transaction costs.
The Foreign Secretaries of the seven South Asian countries accordingly agreed at their first meeting in Colombo (21 - 23 April, 1981) to pursue cooperation in five broad areas, namely agriculture, rural development, telecommunications, meteorology, and health and population services. The Foreign Secretaries also agreed to set up a Committee of the Whole comprising senior officials from the seven countries to identify and report on other areas of possible cooperation. At the first Meeting of this Committee in Colombo, Sri Lanka (31 August - 2 September 1981), the need to expand economic relations, and the need for cooperation in international economic negotiations...