This details the molecular biology lab in AP Biology. Best grade in class.
The AMGEN Lab that we have been doing for the past two weeks consisted of
two parts; Plasmid Fusion and PCR. Each one is a complicated procedure of genetic
engineering, with our own cheek cells and E.Coli supplied by AMGEN. I will start by
explaining the Plasmid Fusion lab.
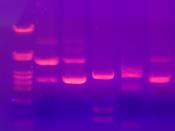
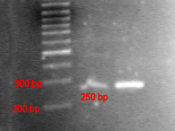
The Plasmid Fusion lab consisted of four major parts; plasmid digestion, gel
electrophoresis, restriction enzyme inactivation and ligation, and the final step, plating out.
But, before I get into that I should define some parts of the lab. The main pieces of genetic
information we will be working with are plasmids. Plasmids are gene sequences found in a
loop outside of the main chromosome. Their main purpose is to code enzymes that digest
antibiotic enzymes. Antibiotics are chemicals that kill bacteria or interfere with their
growth or metabolism.
Cells that have antibiotic resistance have an advantage because
they are able to grow in places that other cells can not.
Our main purpose in this lab is to give an E.Coli cell immunity to the antibacterials,
Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol by genetically doctoring its plasmids. The first step in
doing this is to "cut" the plasmids so that we can ligate the new pieces on later. The DNA
will be cut once twice or not at all because the process does not work all of the time with
all DNA. The part that makes the resistance enzyme will be left in tact and separated into a
smaller section of DNA. We do this so that we can isolate the genome so that we can later
attach other sections of DNA to it. The next step involves checking to see if the
Restriction Enzymes did their job by a process called...