ABSTRACT
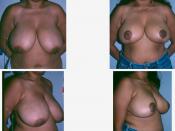
A retrospective study was designed to determine whether patient specific factors - age, smoking and obesity (Body Mass Index) and intra-operative factors, such as weight of tissue removed and duration of operation, influence the complication rates in, patients after reduction mammaplasty. Additionally, it evaluates the long-term results and patient satisfaction after breast reduction. The data was assimilated through a combination of reviewing medical records and telephone questionnaires. We reviewed 67 patients who had bilateral breast reduction at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital (Adelaide) between 1993-98. Mean age of the patient population at the time of surgery was 38.6 years. Mean preoperative weight was 79.5 kg and mean BMI was 30.4 kg/m". The most common presenting complaints were back, neck and shoulder pain, shoulder grooving and skin rashes. 39% of patients also had cosmetic concerns. The inferior pedicle technique was performed in 94% of patients and mean duration of surgery was 135 min.
An average of 740g of tissue was resected per breast. The overall complication rate was 79%. The patient's satisfaction rate with the surgery was 93% and the same percentage of patients reported either an improvement of symptoms or complete resolution. The results of this study shows that increased BMI and preoperative body weight are associated with a significant increase in the complication rate (p= 0.006 and p= 0.018). However, the symptom relief in these patients occurred independently of weight and BMI. The study also shows that smoking increases risk of having late complications by 1.85 times compared with non-smokers (p=0.02). Our results did not find a correlation between age and complication rate (p=0.94). In addition, we found that weight of tissue removed and duration of operation do not influence the post-operative complication rates. Our findings also show that there is no correlation between the amount of...