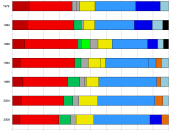
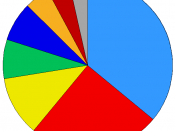
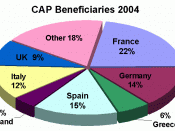
REFORM OF THE COMMON AGRICULTURAL POLICY First of all, I would like to analyse the following questions in my paper: 1. Why does the CAP focus on quantity rather than quality? 2. Why do most European Union agricultural support funds still go to commodity supports (only 10% go to support general rural development) when nearly half the farmers in the EU cannot get a reasonable living for themselves and their families by working full-time in agriculture (i.e. they have to take other part-time work).
3. Why is 45% of the EU commodity support given to arable and field crops, which provide much less employment than livestock or fruit and vegetable production? 4. Why are reduced prices for inputs not reflected in outputs prices? It's important to stress that the CAP is not merely an economic policy but also a social and environmental policy. The EU is firmly attached to its rural environment, which is defined not merely by the landscape but also by the people who live there.
While the CAP was created to ensure an adequate supply of food for European people, its to role has evolved beyond this purpose.
With 7.5 million farms of an average size of forty acres, farming is the backbone of rural EU, from both an economic and social point of view. It is also the farmer who is responsible for maintaining and protecting the rural landscape. There are concerns and demands of European society and more and more the CAP is used to encourage and compensate farmers for fulfilling this multifunctional role.
The 1992 reforms of the CAP (know as McSharry reforms) did not change the Treaty of Rome objectives, though they did weaken the link between production and farm income by introducing a system of direct payments to farmers and a move...