Fungal Pathogenesis
The research seminar, Fungal Pathogenesis explains some physiological pathogenic characteristics in fungi, for example, molds are multi-cellular and yeasts are single oval cells. Fungi, which can cause severe diseases, are single or multi-cellular eukaryotic organisms that lack chlorophyll and vascular tissue with a body mass of branched filamentous hyphae that often produce specialized fruiting bodies. There are approximately 1.5 million of fungi around us and their ability to cause disease is accidental causing as oppose to a virus or other pathogens.
Fungi abilities include physiological barriers that grow in humans, their ability to derive its nourishment from dead or decaying organic matter (saprophytes), they have host defense mechanisms, and dimorphism, a unique ability in which fungi change form based on temperature to get around barriers. If a person inhales for example, the fungus goes under dimorphism to change its form and adapt to the host's temperature levels.
There are two types of virulence factors of fungi that promote colonization and damage the host.
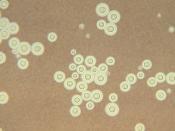
Colonization is achieved by producing polysaccharide capsules to avoid being eating by phagocitic cells, modulation of host immunity, and resistance to phagocytic destruction. Damage to the host is done by the production of destructive enzymes that dematerialize and destroy cells in the host and just by the sheer growth of hyphal growth. The Cryptococcus Neoformans is a deadly fungus that travels to the brain were it starts growing (example of accidental damage), forcing the brain to separate causing severe head aches until it is fatal or to late for recovery.
As mentioned earlier, Cryptococcus is yeast-like fungi of the genus Cryptococcus, commonly occurring in the soil and including certain pathogenic species, such as the causative agent of cryptococcosis. Cryptococcus Neoformans causes an acute, or chronic infection; it generally causes a pulmonary infection but may...