INTRODUCTION
For three decades, satellite communications have been used for public switched telephone network (PSTN) and video broadcasting applications. However, with daily technology advancements made in society and the requirement for global data connectivity, satellites are increasingly being used to provide data communication links at all data rates ranging from 64 Kbps to 155 Mbps (Buchsbaum). Wireless technology allows data to be sent out into space to a satellite and back to earth to provide connectivity among many different network clients. The network can be designed to reach geographically remote sites, where installing land-based lines is not feasible. The only restriction is that the footprint of the satellite must match the area it covers. Satellite networks can use either Ku-band satellites, which use a 3-meter dish (this type of satellites used most commonly for cable television broadcasting) transmitting at 1 GHz, or Ka-band satellites, which uses a 1-meter dish (used less commonly for television broadcasting) transmitting at 2.5
to 3.5 GHz (Shelly).
Frame Relay
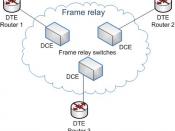
Frame relay is a means of providing a high-speed service that supports LAN interconnectivity, Internet access, file transfer and bandwidth-hungry applications including corporate intranets and desktop video conferencing. It enables devices to be allocated bandwidth on a Committed Information Rate (CIR) and also allows for rapid applications (Invsat.com). In a frame relay network, a geosynchronous satellite (GEOs) is used as the link between frame relay switches, or routers, and the other devices on the network (Shelly).
In a remote land or maritime environment both operators and subcontractors require independent communication support for voice and data applications between the site or ship and the onshore corporate offices (Invsat)
Satellites
A satellite is a repeater in the sky. A source or terminal on the earth transmits a radio signal to the satellite, receives, processes, and retransmits it...

Good
Very informative and nicely written.
3 out of 3 people found this comment useful.