Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy before the fetus is capable of independent life. When the expulsion from the womb occurs after the fetus becomes viable, usually at the end of six months of pregnancy, it is technically a premature birth.
There are two main types of abortions. Abortions may be spontaneous or induced. Expelled fetus weighing less then 0.45 kg (16 oz) or less than 20 weeks gestation are usually consider abortions.
Spontaneous abortions, it is estimated that some 25 percent f all human pregnancies terminate spontaneously in abortion with three out of four abortions occurring during the first three months of pregnancy. The causes of spontaneous abortions are not clearly established. Abnormal development of the embryo or placental tissue is found in about half the cases.
Then there are induced abortions, which is the deliberate termination of pregnancy by removal of the fetus from the womb.
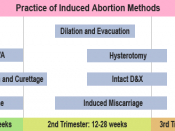
It is currently performed by any of the four standard procedures according to the period of the gestation. Suction or vacuum aspiration is used in the first trimester (up to 12 weeks). This procedure usually takes five to ten minutes on an out patient basis. Pregnancies in the earlier part of the second trimester may be terminated by a special suction, sometimes combined with forceps, in a procedure called dilation and evacuation. The patient may remain in the hospital overnight and may experience a menstrual type of bleeding and discomfort. After the 15 Th. week of gestation saline infusion is commonly used. In this technique a small amount of amniotic fluid is withdrawn from the uterus by means of a fine tube or hypodermic needle through the abdominal wall and is slowly replaced with a strong salt solution. This reduces uterine contractions in about 24 to 48 hours. Late abortions...