In today's business environment, it is important to have strong group interaction. With today's global economy it is more important than ever to have strong interaction between coworkers in order to survive ever increasing competition, especially with the advances in internet based businesses. Building strong groups within an organization pools the talents of many individuals. The pooling of information from different participants creates new ideas in development and production of newer and better products and services.
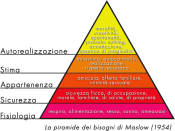
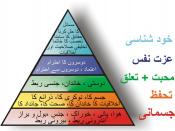
In the following paper, we will explore what groups are and different group theories. Mainly we will also see how Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs applies to professional work dynamics, how the theory designates the team member roles and responsibilities and how participation, leadership, and motivational skills would be demonstrated using Maslow's theory. In additon we will see how the theory affects perspectives on group interaction in the workplace.
GroupsA group can be defined as a small group of people with complementary skills and abilities who are committed to a leader's goal and approach and are willing to be held accountable by the leader.
A group supports the leader's goals and the leader-dominated approach to goal attainment. A group drives individual accountability rather than shared accountability (Mackin, n.d.).
To work successfully in a group we need to sustain meaningful group communication. This communication can be in the form any form, written or vocal. This communication is important for the group to be successful in its goal. Depending of their purpose there are seven different group types. They are primary, social, self-help, learning, service, work, and public groups.
Group TheoriesThere are several types of group theories; they include Fishers Phases, Tuckman's Stages and Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Fisher's Phases - B. Aubrey Fisher developed four main phases of group developments. The four phases are orientation, conflict,