The transmission of words, sounds, images, or data in the form of electronic or electromagnetic signals or impulses. Transmission media include the telephone (using wire or optical cable), radio, television, microwave, and satellite. Data communication, the fastest growing field of telecommunication, is the process of transmitting data in digital form by wire or radio.
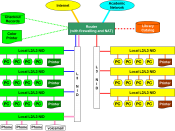
Digital data can be generated directly in a 1/0 binary code by a computer or can be produced from a voice or visual signal by a process called encoding. A data communications network is created by interconnecting a large number of information sources so that data can flow freely among them. The data may consist of a specific item of information, a group of such items, or computer instructions. Examples include a news item, a bank transaction, a mailing address, a letter, a book, a mailing list, a bank statement, or a computer program.
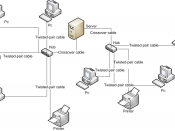
The devices used can be computers, terminals (devices that transmit and receive information), and peripheral equipment such as printers (see Computer; Office Systems).
The transmission line used can be a normal or a specially purchased telephone line called a leased, or private, line (see Telephone). It can also take the form of a microwave or a communications-satellite linkage, or some combination of any of these various systems.
Hardware and Software
Each telecommunications device uses hardware, which connects a device to the transmission line; and software, which makes it possible for a device to transmit information through the line.
Hardware
Hardware usually consists of a transmitter and a cable interface, or, if the telephone is used as a transmission line, a modulator/demodulator, or modem.
A transmitter prepares information for transmission by converting it from a form that the device uses (such as a clustered or parallel arrangement of electronic bits of information) to...