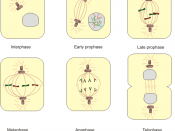
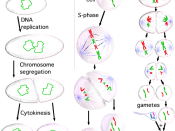The Process of Mitosis is the term used to describe cell division for replication. This process is used for growth and repair within an organism and also for asexual reproduction. There are five main stages to mitosis, called Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. Although the process has been divided up into these stages the process of mitosis is actually continuous.
In Interphase, the first stage, the cell is the original part. All cell organelles are being produced in quantity and the chromosomes (DNA molecules) are being copied exactly. The two identical copies of DNA are called a pair of chromatids and they are linked together by an item called a chromomere.
In Prophase changes to the cell become visible. The chromosomes condense, coiling up to about 5% of their original length. The centrioles move to the opposite poles of the cell and small microtubules around the centrioles become visible.
The nuclear membranes and nucleolus disintegrate after passing their nucleic acids to certain pairs of chromatids. Now a spindle forms, this is also made out of microtubules.
During Metaphase, the chromosomes move towards the equator of the spindle, attaching themselves horizontally by the centromere to the spindle's filaments. The chromatids then pull slightly away from each other at the centromere towards the opposite poles of the cell. Some spindle fibers run from pole to pole while others from pole to equator. In this phase, there is no nuclear membrane at all.
Anaphase, the next step, is very quick. The pairs of chromatids are separated and each chromatid is pulled towards each opposite pole by the spindle fibers by a ratchet-like mechanism. This process requires energy so the ATP stored is now used up. They split apart by the centromere breaking into two. Each centromere divides into two so...