Abstract:
The purpose of this paper is to research three separate organizations representing three different economic sectors, and provide a description of the need for customer driven quality in each organization. Additionally, construct a comparison matrix outlining the differences between the strategic roles of Total Quality Management (TQM) within each of the organizations and finally asses the importance of leadership within each of these organizations as it relates to quality.
Total Quality Management (TQM) Survey Paper
The organizations of focus represent the manufacturing sector, non-profit service sector, and the government sector. Each of these economic sectors has different values in quality of customer relations, as well as, strategies towards TQM based on their customer needs and their level of development within their sector.
Manufacturing
The first organization of focus which represents the manufacturing sector is MESA Products, Inc. MESA Products, Inc. is a small, privately held business that designs, manufactures, and installs cathodic protection systems which control the corrosion of a metal surface.
Mesa Products is a small company with about 70 employees and its company headquarters are located in Tulsa, Oklahoma with branch offices in Tallahassee, Florida and Houston, Texas and Huntington Beach, California.
MESA was established with a general philosophy of providing a quality product at a fair price. Quality has always been a priority at MESA. The company's consistent growth is a direct result of our dedication to customer satisfaction. Mesa Product's Inc was a Malcolm Baldrige Award recipient in 2006 because of such highlights as:
MESA Products, Inc., has demonstrated sustained sales growth from 1985 to 2006. Sales have increased from less than $2 million in 1985 to over $25 million in 2006. In a mature industry with limited new business, MESA has achieved this growth primarily through gains in market share from its competitors
MESA's current performance in all 17 areas of satisfaction on its third-party Customer Satisfaction Survey exceeds that of its best competitor. From 2002 to 2005, its overall level of customer satisfaction increased from 80% to 88%, surpassing the best competitor and American Customer Satisfaction Index of Energy Utilities (ACSI) levels of approximately 73%.
Lean manufacturing concepts have helped MESA achieve cycle time and productivity improvements. For example, lead time for the sales order entry process was reduced by 30%, and error rates were reduced by 50%. On-time shipments are now at 97%.
In 2005, MESA supported 17 key community activities, with more than 50% of employees participating in activities such as Food for Families, the Oklahoma Blood Institute, and Adopt-a-Family, and donated $45,000 to eight community organizations, an average of more than $600 per employee.
Results from MESA's employee satisfaction survey show performance levels for the 17 surveyed attributes are 20% or more above the industry normative comparisons, and most meet or exceed the top 10% of the group of companies included in the survey conducted by a third party research organization (Mesainc.com, 2007).
Mesa Products quality and service standards have moved the company to a new level of performance and have enabled MESA to set service standards for the entire cathodic protection industry.
The MESA Value Promise (MVP) guarantees customer satisfaction. Customer driven quality is required in order for Mesa Products Inc to retain its large market share in it' industry. The company's leadership must insure improvement in their products in order to increase their market share. More specifically, Mesa Products has many customers and their satisfaction is critical. As such, their needs must be constantly studied and product modified in order to insure complete satisfaction.
The importance of quality in today's world has never been more evident. As a result, MESA formalized the company's Total Quality Management Program in 1993. MESA's Quality Commitment is to provide products and services that meet the needs and expectations of our customers. MESA is committed to being the industry leader in quality and service, assuring our customers full satisfaction. Mesa rolled out its MESA Value Promise program in 2003 to emphasize the commitment to the industry.
MESA's Quality Policy is summarized by ACT ~ Accurate - Continuously Improving - Timely (Mesainc.com, 2007).
Service
The second organization of focus represents the non-profit service sector Premier, Inc.. Premier, Inc., is a healthcare strategic alliance entirely owned by not-for-profit hospitals and health system organizations. The 200 owners operate or are affiliated with more than 1,500 hospitals and thousands of non-hospital sites such as nursing homes and ambulatory centers. Owners participate to share needed services and programs aimed at improving clinical quality and cost-effectiveness.
Premier, Inc was selected as the 2006 Malcolm Baldrige Award Winner for the services sector with highlights such as:
From 2002 to 2006, consolidated pre-tax operating income increased from approximately $140 million to approximately $223 million in 2006, exceeding or equaling that of Premier's largest single competitor. Operating margin percentage increased from 35% in 2003 to 50% in 2006 and exceeded that of Premier's largest single competitor in all years. In addition, operating expenses have remained well below those of Premier's top competitor.
Savings and cash returns to Premier's hospital owners have increased from approximately $180 million in 2002 to $804 million in 2006.
As an indirect measure of customer-perceived value, retention of hospital members has remained strong and increased from 94% in 2002 to approximately 97% in 2006.
Premier has taken a leadership role in promoting best practices in ethical conduct, transparency, and accountability within its industry and created the Healthcare Group Purchasing Industry Initiative to promote and monitor best ethical practices in purchasing for hospitals and other health care providers.
Premier utilizes systematic approaches to focus on the career development of employees, including the Ph.D. Program, The Leadership College, and tuition reimbursement.
Premier's Informatics Business Unit market share, as measured by number of clients, exceeds its nearest competitor by more than two-fold, making it the largest provider in the nation for comparison data for hospitals and related organizations.
Focus on people: showing concern and respect for all with whom we work, building collaborative relationships with the community, our customers, co-workers, and business associates (Sorra, 2004)
Premier helps members and clients reduce costs and enhance revenue while improving clinical processes and outcomes. Premier believes that the greatest opportunities for improvement often lie in process improvement, but they also can be the most difficult to achieve.
Some defining characteristics of Premier Inc include: a strong sense of purpose and values, a clear long-term goal, the capacity to visualize what can be accomplished, and to act toward that picture over time (Premierinc.com, 2007).
Government
Finally, the third organization of focus representing the government sector is the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Total quality management is an accepted and proven management technique in the private sector, but it only recently found acceptance in the government sector. In the face of well-documented and well-publicized quality problems, the Internal Revenue Service introduced a quality improvement program in 1986 and reaffirmed its commitment to quality with A Plan for Improving Quality, Customer Service, and Organizational Performance in 1991. This strategic plan outlines the top-down approach necessary to transform the IRS into a quality organization that consistently produces and delivers services exceeding customers' needs and expectations.
The IRS has three major goals: Enhancing quality and productivity through its business processes, reducing the taxpayer burden and improving voluntary compliance (Chen, 1994). It plans to achieve these goals through a combination of quality improvement initiatives and modernization efforts including
Increasing the quality of services provided to taxpayers through employee empowerment--equipping workers with appropriate skills, resources and authority to do the job right.
Adhering to the highest standards of professional and ethical conduct through active leadership that both clarifies and communicates expectations for ethical behavior and also fosters a climate supporting and demonstrating a commitment to such behavior.
Embracing and managing diversity to capitalize on the different experiences, values, perspectives and concerns in the work force.
Implementing the Compliance 2000 initiative.
TQM and TSM (Tax System Modernization). The specific objectives of TSM include
Modernizing tax document input processing.
Minimizing paper processing.
Making taxpayer information readily accessible to IRS employees.
Reducing recordkeeping and tax administration costs.
Increasing the security and privacy of sensitive taxpayer information.
Ensuring adequate capacity and flexibility to meet the IRS's future needs. (IRS, 2006)
The IRS is dedicated to making sure people understand their responsibilities in the tax process. "The IRS maintains a customer-oriented focus by routinely soliciting information about the needs and the characteristics of its customers and implementing programs based on that information."(IRS, 2006) Their goal is to continue to improve customer satisfaction ratings and this is possible because of Restructuring and Reform Act of 1998. (Chen, 1994)
Total Quality Management
The strategic role of TQM with the organizations outlined is very similar in some cases, but also a bit different due to the size of the organization, the customer, and mission and vision of each organization. To compare and contrast the strategic roles within the organizations a matrix will be used compare the following TQM roles: Mission and Vision, Customers, Management, Employees, Products, Culture, and Quality Process Improvements .
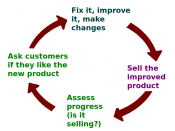
In each of these organizations, the importance of leadership directly relates to quality, Business and industries are beginning to understand that poor quality costs companies and that improved quality of goods and services goes hand in hand with improved productivity, lower costs, and increased profitability. Improved management understanding of the factory floor, worker involvement in quality, and greater emphasis on statistical process control can lead to dramatic improvements in the cost and quality of manufactured products.
The concept of quality improvement is directly applicable to small companies as well as large, to service industries as well as manufacturing, and to the public sector as well as private enterprise. in order to be successful, quality improvement programs must be management-led and customer-oriented, and this may require fundamental changes in the way companies and organizations do business.
References:
Chen, Al Y.S. (July, 1994) TQM at the IRS - Total Quality Management. Journal of Accountancy. Retrieved from the web on February 19, 2007 from: http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m6280/is_n1_178/ai_15563484
IRS (2006) IRS Customer Service. Report to the Chairman, Subcommittee on Oversight Committee. Retrieved from the web on February 19, 2007 from: http://www.gao.gov/archive/1999/gg99088.pdf
Mesaproducts.com (2007). Mesa Products Inc Webpage. Retrieved from the web on February 19, 2007 from: http://www.mesaproducts.com/homepage/homepage.htm
Premierinc.com (2007) Premier Inc Webpage. Retrieved from the web on February 19, 2007 from: www.premierinco.com/about/index.jsp
Sorra, JS. (September 2004). Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.. Retrieved from the web on February 19, 2007 from: http://www.premierinc.com/all/safety/culture/downloads/2_hospcult111004.doc


Nice Quality
This paper was written great and explained all three organizations well.
0 out of 0 people found this comment useful.