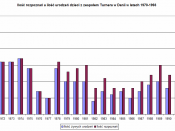
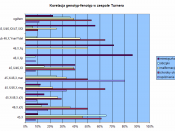
Turner's syndrome
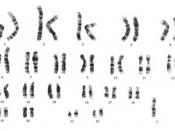
Definition: Turner's syndrome is a genetic disorder where affected woman only have one X chromosome. This results in developmental abnormalities and infertility.
Causes: Turner's syndrome is caused when one normal chromosome is present in a female's cells and the other X chromosome is either missing or the structure is altered. Most cases are not inherited but occur as a random event when the reproductive cells are being formed in the affected person's parent. This occurs due to nondisjunction (an error in cell division). If one of these cells are being used in the genetic makeup of a woman, the individual will only have one X chromosome and will be missing the other. This could affect the SHOX chromosome which is responsible for bone growth and development. Having one less copy can cause a woman to be shorter and have skeletal abnormalities. They could also have ovarian failure and learning disabilities.
Symptoms: The symptoms at birth or during infancy could include; Wide or web-like neck, Receding or small lower jaw, High, narrow roof of the mouth (palate), Low-set ears, Low hairline at the back of the head, Drooping eyelids, Broad chest with widely spaced nipples, Short fingers and toes, Arms that turn outward at the elbows (cubitus valgus), Fingernails turned upward, Swelling of the hands and feet, especially at birth, Slightly smaller than average height at birth, Delayed growth and Sensitivity to noise. In young woman or adolescents the woman will not have growth spurts which will result in a short stature. Their sexual development is put off due to failure to begin sexual changes at puberty which results in an early end to menstrual cycles and for most women with Turner's syndrome the inability to conceive a child.
Prejudice: A woman with Turner's syndrome looks different to others.