Summary
The FED has mentioned that the economy has left the soft spot behind and suggested that more interest-rate increases are to come. The fear of inflation was contained mentioned Mr. Greenspan, but did cite other risks such as: slowing productivity growth and evidence of increased pricing power. The federal funds rate has increased to 3% on its overnight loans since last June and will likely continue to increase.
Definition
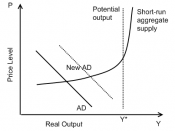
This article is an example of monetary policy and its effect on aggregate demand. Aggregate demand was described in full in article #3. Remember, that when an economy edges toward recession, one or all of the components of aggregate demand lie below potential. To find full potential, one must look at the long run aggregate supply curve (LRAS) and the short run aggregate supply curve (SRAS). These definitions were also given completely in article #3. The point where the SRAS path meets the LRAS path is called full potential.
If the aggregate demand curve intersects to the left of this point, we say there is a recessionary gap. This is the gap that the government will try to reduce by using fiscal and monetary policy. Monetary policy injects money into the economy in order for consumption and investment. The Federal Reserve, a central bank that is an agency of the Federal government, conducts monetary policy. This bank has six duties defined through congressional legislation: conduction monetary policy, supervising financial institutions, serving as a lender of last resort to financial institutions, providing banking services to the U.S. government, issuing coin and currency, and providing financial services to commercial banks. These six duties essentially give the FED ultimate control over the money supply in the United States. In fact, the liabilities of the FED (Federal Reserve Notes) serve as cash...