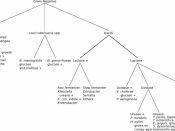
This investigation was completed as a partial requirement for the Honors Biology course of Franklin High School in Franklin, Pennsylvania during the 2003-2004 school year. The investigation was conducted to prove the following hypothesis: Administering different antibiotics to Streptococcus salivarius will prohibit growth at different rates.
Antibiotics are substances produced by living organisms that inhibit the growth of microorganisms. Bacteria manufacture substances to inhibit or kill other microbes. Stated in Antibiotics and Disinfectants, "some antibiotics are used widely therapeutically but some are also too toxic to be of any medical value." The 1940s were the "dawn of the antibiotic era"(qtd. in Puglia).
Penicillin, which is often referred to as the "wonder drug", was accidentally discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. A Scottish physician and bacteriologist, Fleming was throwing out old culture plates that were contaminated with mold where a bacterial culture had stopped growing. He noticed a strange growth pattern, a clear area around the mold where the bacterial culture had stopped growing.
This strange growth pattern turned out to be Penicillium motatum, a mold that inhibits the growth of bacterium. Penicillium is a bactericidal which inhibits cell wall synthesis. Ampicillin is also a bactericidal and inhibits cell wall synthesis as well. The cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. Penicillin prevents the synthesis of the intact peptidoglycans, this causes the wall to collapse and the cell then breaks. Gram positive bacteria have thicker cell walls and more peptidoglycans so therefore, they're more susceptible to Penicillin than Gram negative bacteria. Humans do not have peptidoglycans so Penicillin has very little toxicity for the host cells (Puglia).
Erythromycin's source is Streptomyces erythraeus. It has a bacteriostatic effect and inhibits protein synthesis. This takes places due to the structural difference between ribosomes in bacterial and human cells. There are certain antibiotics...