Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
Originated from
Is produced by micro-organisms in times of physiological stress, and is used by micro-organisms as a chemical energy store for times when other energy more common molecules are not readily available. A polyhydroxyalkanoate (a linear polyester produced naturally by bacteria fermenting sugars and/or lipids), it belongs to the "Polyesters", and is a bacteria based plastic.
First discovered
First characterised and isolated by French microbiologist Maurice Lemoigne, in 1925.
Chemistry
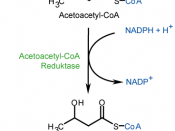
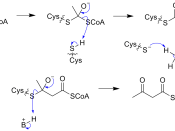
It is biosynthesised (like a chemical reaction produced from simple molecules, except it occurs within an organism, and tends to be "catalysed" by enzymes within said organism) by the condensing of two molecules of acetyl-CoA to create acetoacetyl-CoA, which is then reduced to hydroxybutyryl-CoA. This is the monomer that PHB is composed of.
Acetyl-CoA is a complex molecular structure primarily composed of Oxygen, Hydrogen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur. (molecular formula is C21H36N7O16P3S).
The poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB) form of PHB is probably the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoate, but many other polymers of this class are produced by a variety of organisms: these include poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB), polyhydroxyvalerate (PHV), polyhydroxyhexanoate (PHH), polyhydroxyoctanoate (PHO) and their copolymers (a polymer derived from two or more monomers).
Uses
Polyhydroxybutyrate is commercially valuable as a plastic material because of its useful physical properties. Its properties are very similar to polypropylene, except it is biodegradable where PP is not. (They also have remarkably different chemical structures, despite having similar physical properties.)
Properties
Stiff and brittle
High degree of crystallinity
A high melting point (180 degrees Celsius)
Rapidly biodegradable.
Pros
Is very similar to polypropylene, despite having a very different chemical structure, except it is biodegradable where polypropylene is not.
Cons
Comparatively high production costs (higher than plastics produced from petrochemicals), and its brittleness which cannot handle high impact.