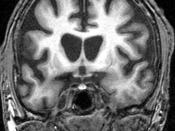
Huntington's Disease
Huntington's Disease (HD) is an inherited conditions characterized by abnormal body movements, dementia, and psychiatric problems. Huntington's Disease is a progressive disorder involving degeneration of nerve cells in the brain. It is one of the more common inherited brain disorders. About 25,000 Americans have it and another 60,000 or so will carry the defective gene and that binds itself to the Huntington molecule only in the brain. Both conclude that Huntington Disease is a mutation that causes damage to brain cells further in a person's life.
HD is inherited as a single faulty gene on chromosome # 4. There is a part of the gene that is repeated in multiple copies. The greater the number of repeats, the more likely it is that the person will develop symptoms and the greater the chance they will occur at a younger age. The disease may occur earlier and more severely in each succeeding affected generation because the number of repeats can increase.
Every child of a parent with the disorder has a 50% chance of inheriting Huntington Disease. Symptoms do not usually appear until adulthood, typically between ages 35 and 50 years old, but this depends on the number of repeats found in the gene so it may also appear in younger people. In children it may appear to be Parkinson's disease with rigidity, slow movements and tremor. There is progressive loss of mental function, including personality changes, and loss of cognitive functions such as judgment, and speech. Abnormal facial and body movements develop, including quick jerking movements.
The symptoms for Huntington Disease in older people are behavior changes the person might feel irritably antisocial and restlessness. The person may be suffering from psychosis, paranoia, and hallucinations. Loss of memory, judgment and confusion or disorientation, unsteady quit, progressive developments of...