Introduction
Aim: The objectives of this lab experiment are to observe the process of emulsification and to compare the actions of pepsin and saliva (Amylase).
Background Information: The function of the human digestive system is to digest food that is taken in. Digestion is the process by which large, solid substances such as fats and proteins are broken down into small soluble substances. Digestion consists of two main processes, physical digestion and chemical digestion. Physical digestion is the breaking down of foods by physical means, i.e., not changing the substance itself, only its state. Physical digestion takes place mainly in the mouth and stomach, where it is chewed, grinded, and mixed. Chemical digestion breaks down large molecular substances into simpler substances, changing their chemical properties and structure, using digestive enzymes. Chemical digestion occurs mainly in the stomach and small intestine.
Saliva containing amylase acts on starch to break it down into maltose, in the mouth, starting the process by which starch is broken down.
After it has been swallowed, the food passes down the oesophagus into the stomach.
The stomach consists of gastric glands that produce gastric juice, which contains pepsin, an enzyme that dissolves proteins into simpler substances called polypeptides. After spending three or four hours in the stomach, the food travels to the small intestine. The small intestine is where digestion is completed and its soluble products are absorbed.
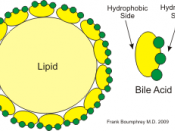
The small intestine receives fluid called bile from the liver. Bile consists mainly of bile salts and sodium hydrogen carbonate. The bile is slowly secreted into the first part of the small intestine, the duodenum. This is where emulsification takes place. Emulsification is a physical process whereby large globules of fat are broken down into smaller globules and made water soluble, using bile salts.
Bile salts are...