STEM CELL RESEARCH
Research on stem cells is advancing knowledge about how an organism develops from a single cell and how healthy cells replace damaged cells in adult organisms. Stem cells are one of the most fascinating areas of biology today. But like many expanding fields of scientific inquiry, research on stem cells raises scientific questions as rapidly as it generates new discoveries.
The NIH developed this primer to help readers understand the answers to questions such as: What are stem cells? What different types of stem cells are there and where do they come from? What is the potential for new medical treatments using stem cells? A. What are stem cells and why are they important?
Stem cells have two important characteristics that distinguish them from other types of cells. First, they are unspecialized cells that renew themselves for long periods through cell division. The second is that under certain physiologic or experimental conditions, they can be induced to become cells with special functions such as the beating cells of the heart muscle or the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas.
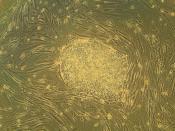
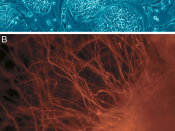
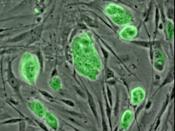
Scientists primarily work with two kinds of stem cells from animals and humans: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells, which have different functions and characteristics that will be explained in this document. Scientists discovered ways to obtain or derive stem cells from early mouse embryos more than 20 years ago. Many years of detailed study of the biology of mouse stem cells led to the discovery, in 1998, of how to isolate stem cells from human embryos and grow the cells in the laboratory. These are called human embryonic stem cells. Stem cells are important for living organisms for many reasons. In the 3 to 5 day old embryo, called a blast cyst, a small group of...