The most structurally diverse collection of organisms is the kingdom Protista. Most protists are unicellular, microscopic organisms, but a few are complex and multicellular. Protists are also the most diverse in terms of their life cycles, which can involve asexual or sexual reproduction. Composed of metabolically diverse organisms, the kingdom Protista contains the ancestral life-forms that gave rise to the three kingdoms of multicellular organismsþthe fungi, the plants, and the animals.
Amoebas, members of the phylum Rhizopoda, are protists that live in fresh and salt waters and are especially abundant in soil. Because an amoeba has no cell walls or flagella, it is extremely flexible. It moves through its environment using extensions of cytoplasm called pseudopodia. Pseudopodia are also used to surround and engulf food particles in the process of endocytosis. Meiosis and sexual reproduction do not occur in amoebas. They reproduce by fission, simply dividing into two new cells.
The majority of amoebas are free-living, but some species are parasites, which are transmitted by contaminated food or water.
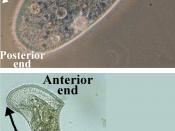
As the name ciliates indicates, all members of the phylum Ciliophora have large numbers of cilia, usually arranged in long rows down the body or in spirals around it. Ciliates are complex unicellular heterotrophs. The body wall of ciliates is a tough but flexible outer pellicle that enables the organism to squeeze through or move around many obstacles. The pellicle consists of an outer membrane with numerous fluid-filled cavities beneath it. Ciliates, such as Paramecium, form vacuoles for ingesting food and regulating their water balance. Most ciliates have two types of nuclei within their cells: small micronuclei and larger macronuclei. The micronuclei contain normal chromosomes that divide by mitosis. Macronuclei contain small pieces of DNA derived from micronuclei. Reproduction is usually by mitosis, with the body splitting in half. Most ciliates...


"Kingdom Protista and the Phyla Under It"
This is a somewhat thorough paper but at the same time it touches only the surface of the Kingdom of Protists. Well-done overall.
3 out of 3 people found this comment useful.