I am going to investigate the enthalpy change of combustion for the alcohol homologous series. I will investigate how alcohols with increasing number of carbons affect the enthalpy change when an alcohol goes under combustion.
The energy that alcohols release when being used is called the enthalpy change of combustion. This is defined as
"Standard enthalpy change of combustion, is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen under standard conditions (298K, 100 KPa and 1 Molar) with all products in their standard state" (Collins advanced Chemistry)
Enthalpy is the total energy content of the reacting materials. Enthalpy is given the symbol H. the only was to measure enthalpy is the measure the change in energy before and after as energy cannot be measured directly.
The symbol in the notation used for standard enthalpy change under combustion means that the combustion has taken place under standard conditions, s.t.p.
Therefore the statement DHq =-286 kJ mol-1 means the enthalpy change of the combustion of hydrogen when one mole of hydrogen is completely burnt in oxygen under standard conditions with reactants and products in their standard states at that temperature.
CH4 (g)+2O2 (g) CO2 (g)+ 2H2O(l)
DHq= -890 kJ mol-1 meaning that the stored reactants methane and oxygen are higher than the stored energy of the products of the reaction, carbon dioxide and water and the difference in energy is released to the surroundings when the methane and oxygen react. The reaction of methane can be displayed in the form of an energy level diagram. The enthalpy change is negative because the reactants loose energy, therefore all exothermic reactions will have a negative value for their enthalpy change. Energy is not actually made in this reaction, it is only transferred from one state to another,
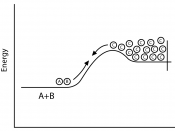
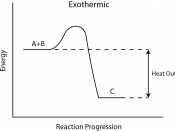
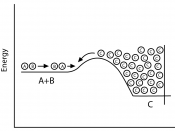
!
What kind of essay is this? Half the work is scattered listings? And the writing itself doesn't present a clear thought-process.
0 out of 0 people found this comment useful.