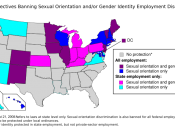
To discriminate is to make a distinction. There are several meanings of the word, including statistical discrimination, or the actions of a circuit called a discriminator. This article addresses the most common meaning of the word, social, racial, religious, sexual and ethnic discrimination.
1.1 DEFINITION
Discrimination involves formally or informally classifying people into different groups and according the members of each group distinct, and typically unequal, treatments, rights and obiligations. The criteria delineating the groups, such as gender, race, or class, determine the kind of discrimination.
Discrimination generally refers to treating one group of people less well than another on such grounds as their race (racism), gender (sexism), religion (religious discrimination), height, ethnic background, national origin, disability, sexual orientation, preference or behavior, or political views. Discrimination on the basis of such grounds as subcultural preference (Punks, Hippies, Mods vs. Rockers) is also common.
The effects of discrimination span the spectrum from mild, such as slow or unhelpful retail service, through racial and ethnic slurs, denial of employment or housing, to hate crimes and genocide.
Use of the term carries the implication that the factors on which the discrimination is based are intrinsically irrelevant to the decision being influenced. Generally, the aggrieved group is considered by the discriminator as inferior to others.
1.2 INSTITUTIONALIZED DISCRIMINATION AND RESPONSES
Many governments have attempted to control discrimination through civil rights legislation, equal opportunity laws and institutionalised policies of affirmative action (called reverse discrimination by its opponents).
Some governments have formalized and supported discrimination. Examples include apartheid in South Africa, institutionalized racial segregation in the USA from the Civil War through the 1960s, the "Jewish problem" in Nazi Germany, or re-education camps in some communist countries.
Even in western or more secular countries, the government have discriminatory practises. The most obvious is that the government...