Spina bifida is a neural tube defect, one of the most common of the congenital malformations. The other two types of neural tube defect, includes anencephaly and cranium bifidum. The backbone and the spinal cord do not close before birth. This results in the spinal cord and it covering membranes to protrude out of the back. Spina bifida is a Latin term meaning "split spine"�; the defect is also known as "open spine"�. This defect develops during the first three to four weeks of a pregnancy. Spina Bifida takes into two main forms, spinal bifida occulta, and spina bifida cystica. Spina bifida cystica are the more serious defect, where there is a protrusion of a fluid-filled sac.
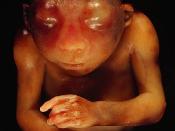
Spina bifida cystica affects one in every 2,000 to 2,500 babies. Approximately 90% are born with the most serious condition of this defect, Myelomeningocele. Myelomeningocele means, "bulging of the meninges and the spinal cord"�.
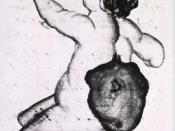
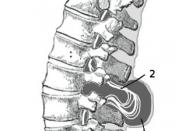
For this defect, the sac not only contains tissue and cerebo-spinal fluid but also nerves and parts of the spinal cord. Therefore, the spinal cord is not properly developed or is damaged, which can cause some degree of paralysis and loss of sensation below the damaged vertebrae. In addition, many adults and children with this condition have problems with bowel and bladder control.
Another type is meningocele; this is the less common form meaning, "bulging of the meninges,"� (meninges are three-layered membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord). This occurs when the opening in one or more vertebras opens enough to allow the meninges to get through. When the meninges bulges through the skin a lump if formed which can be as small as a grape or as large as a grapefruit. The nerves are not usually affected and are still able to function therefore...