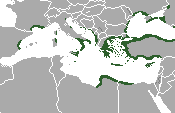
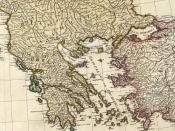
Ancient Greece was the birthplace of Western civilization about 3rd millennium to the 1st century. They were known for their philosophy, architecture, drama, government, and science. Geographically it indicates the heartland of Greek communities on the north coast and nearby islands of the Mediterranean Sea. Culturally, though it indicates how the ancient Greeks spoke. How they worshipped and understood the physical world.
Greek civilization developed in small city-states. City-states had citizens. These citizens were strongly patriotic and many of them took part in public affairs. The world's first democratic government was established by the most advanced city-states. Athens and Sparta were known for the best city-states.
The city-states never united as a nation. However, they still shared a common language, culture, and religion. Greeks called their land Hellas and themselves Hellenes. They thought they were different from others. They called outsiders barbarians.
Greek writers created forms of expressions, by human personalities and emotions.
The Greek World
The territory of ancient Greece consisted of a mountainous peninsula that went into the Mediterranean Sea west coast of Asia Minor and nearby islands. A strip of land separated the southern part of Greece, called the Peloponnesus, to the northern part of the mainland.
THE LAND
The most fertile land was found in small valleys and along the coast. At the center of each city was an agora. This was a market place or where meetings were held. Most cities had wall surrounding for protection from invaders.
The weather in ancient Greece was warm, and dry. The summers were hot and winter temperature dropped below zero. Rainfall ranged from as much as 50 inches on the west coast, to less than 20 inches on the east.
The mountains provided limestone and marble for building construction and clay for making pottery and bricks. The...