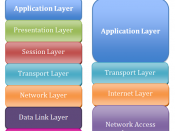
Description of OSI layersOSI ModelData unit Layer FunctionHostlayers Data 7. Application Network process to application6. Presentation Data representation and encryption5. Session Interhost communicationSegment 4. Transport End-to-end connections and reliabilityMedialayers Packet 3. Network Path determination and logical addressingFrame 2. Data Link Physical addressing (MAC & LLC)Bit 1. Physical Media, signal and binary transmission[edit] Layer 7: Application LayerMain article: Application LayerThe application layer is the OSI layer closest to the end user, which means that both the OSI application layer and the user interact directly with the software application. This layer interacts with software applications that implement a communicating component. Such application programs fall outside the scope of the OSI model. Application layer functions typically include identifying communication partners, determining resource availability, and synchronizing communication. When identifying communication partners, the application layer determines the identity and availability of communication partners for an application with data to transmit. When determining resource availability, the application layer must decide whether sufficient network resources for the requested communication exist.
In synchronizing communication, all communication between applications requires cooperation that is managed by the application layer. Some examples of application layer implementations include Telnet, File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
[edit] Layer 6: Presentation LayerMain article: Presentation LayerThe Presentation Layer establishes a context between Application Layer entities, in which the higher-layer entities can use different syntax and semantics, as long as the Presentation Service understands both and the mapping between them. The presentation service data units are then encapsulated into Session Protocol Data Units, and moved down the stack.
This layer provides independence from differences in data representation (e.g., encryption) by translating from application to network format, and vice versa. The presentation layer works to transform data into the form that the application layer can accept. This layer formats and encrypts data...