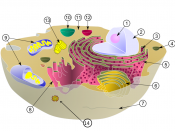
Golgi
The golgi is like a carrying crate that is designed to transport matter collectively around the cell to where it is needed or even to other cells if the situation arises. The golgi is simply a membrane sack with small tentacle like appendages that uses active transport to propel itself around until it reaches its destination. The golgi is able to hold everything from starch (carbohydrates that can't be stored in the chloroplasts), waste and proteins.
Centrosome
The centrosome is a circular structure much like the golgi that is used to contain the chromosomes of the cell. During cellular mitosis, the centrosome would split in half and the short tentacle like protrusions that called microtubules would stretch out to opposite parts of the cell where both sections are exactly the same. When the cell splits, the centrosome would divide into two half circles with tentacles coming out of the circular ends but then it would rebuild its opposite part, sometimes with a slight "mutation" (the essence of evolution) and the two cells would carry on with what they are doing.
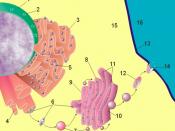
Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumThe rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) is a thin membrane like structure that surrounds the outside of the nuclear membrane. The rough ER is pretty much where protein synthesis in the cell occurs. The basic process is that RNA (copies of DNA fragments) is sent out, coded in a "trianary" system (simply put 0, 1, and 2) where it attaches itself to one of the walls in the rough ER. Next, carrier proteins are released that are coded to certain parts of the RNA and then forced to get the required enzymes. These enzymes are then stacked down into enzyme chains to create proteins, if the enzymes grouped together are in an acceptable order; the protein would...
Not a bad essay
it was a lot to read but it explained a lot
3 out of 3 people found this comment useful.