Mitosis
The human body is made up of millions and millions of building blocks. These building blocks are called cells. Cells are the most basic parts of life. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems, and when you have every one of these put together in perfect structure and organization the end result is what a human being is. The most important of every one of these features is the cell. The cell controls all the living functions such as movement, sight, and everything else you can perform. Every single action. Voluntary or involuntary.
A person starts out in the very beginning as one cell. This one cell becomes two cells. These two cells become four cells. These four cells become eight cells. The process is never ending. The process doesn't end when you turn 100 years old because you're body is always growing no matter what.
The growing process is the most important function that takes place in your body. Whether you want to believe it or not. When you get cut on your arm, you're body's cells duplicate to heal and repair the wound. When you break a bone in your body, the cells duplicate to heal and repair the fracture. Or when you hit puberty and your skin tries to hold all the cells that are currently duplicating, the skin expands with the growth of new cells for a growth spurt. The process is never ending. This growth, or reproduction of the cells is one of the most exciting processes of microbiology. It is called mitosis.
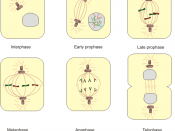
Mitosis is the asexual reproduction of a eukaryotic cell to make two completely new identical daughter cell replicas of the parent cell. Mitosis is composed of four unique phases. The phases are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Before mitosis begins the most important thing that happens is that the chromosomes are duplicated in the nucleus. The first and beginning stage of mitosis is prophase. During prophase, many changes begin to happen throughout the whole cell. Beginning in the nucleus, the chromosomes, two sister chromatids, begin to contract and become smaller. The nuclear envelope surrounding the nucleus breaks up and the fragments left disappears and the centrosomes start to move to opposite poles, or the ends of the cell. The last thing to happen is the spindle microtubules extend and attach themselves to the centromeres, or to the middle of the chromosomes. These spindle microtubules force the chromosomes to move toward the center of the cell.
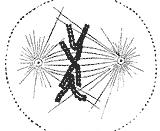
The second stage of mitosis is called metaphase. When the chromosomes, pulled by the spindle's microtubules, reach the center of the cell and line up along the middle of the cell this is the start of metaphase. The centromeres are lined up along the metaphase plate. The spindle microtubules begin to pull the two sister chromatids apart from each other. Metaphase is the shortest of the four phases and the chromatids are not fully separated until the next phase of mitosis.
The third stage of mitosis is called anaphase. Anaphase begins when the two chromatids fully separate from each other and are pulled by the microtubules to the opposite ends. When this happens the spindle microtubules shorten and the microtubules not attached to the centromeres are lengthened. The poles are moved farther away from each other making the cell elongated. Anaphase ends when all the chromosomes reach both ends of the cell.
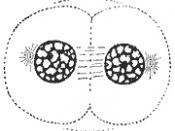
The last and final stage of mitosis is called telophase. During telophase, the elongation of the cell continues. Daughter nuclei appear at the two poles of the cell. The chromosomes expand and lengthen as they were before they contracted in prophase. The nuclear envelope fragments reappear and begin to form around the expanded chromosomes and the nucleoli also reappear. Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, occurs during telophase too. This occurrence begins when the elongation of the cell has stopped and the cell begins to pinch in at the middle. The pinching in of the cell is also called the cleavage furrow. When the pinching of the cell has completed the end result is the two identical daughter cells that have formed.
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase make up the process of mitosis.
When the new daughter cells have formed, they gather food and grow. They keep growing until they are mature enough to begin mitosis again. Mitosis is a never-ending process, which continues to go on and thrive in every living organism. It is the most frequent form of reproduction occurring among every single multi-celled eukaryotic organism that scientists have encountered. It is called mitosis.