Fallacy Paper
In order to recognize what a fallacy is we must understand what an argument is. If an argument contains a fallacy, then the conclusion will not necessarily be proven. Some fallacies are just unintentional, but they can also be used to trap a listener or reader into believing faulty conclusions. This paper will describe three logical fallacies and give an example of each. A fallacy is an error in reasoning. A fallacy is an "argument" in which the premises given for the conclusion do not provide the needed degree of support. A relevance fallacy is a relevance argument that is invalid, could have all true premises and still have a false conclusion. An insufficient fallacy is less formal than a relevance fallacy. They are "arguments" which appear to be insufficient arguments, but the premises do not provided enough support for the conclusion. In such cases, even if the premises were true, the conclusion would not be more likely to be true (www.datanation.com/fallacies).Every
day, we are persistently showered with information, information which we need and/or do not need. Television and radio are some of the prime culprit. With the internet, things seem verging out of control, not to mention the nonstop rumbling of those around us such as our employers, friends and relatives.
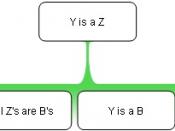
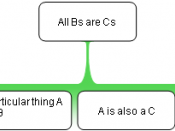
Most rational fallacies can be grouped into three general categories. These are material fallacies, fallacies of relevance, and verbal fallacies. Anyone presenting an argument uses both premises and presuppositions. Premises are the starting points of an argument that can be proven, while presuppositions are the underlying assumptions that cannot be proved or disproved. Presuppositions are unavoidable because of human bias (D. E. Chittick, 1997, pp. 92-93). Since the presuppositions cannot be proved or disproved, they must be taken on faith. It is important to identify these...