Iraq is a country that is on the rise. After being crushed by allied troops for their
invasion of Kuwait, they have begun the slow rebuilding process. In this report, I will
discuss the basic geographic features of Iraq, and other various important features such as
mineral wealth, vegetation, ect.
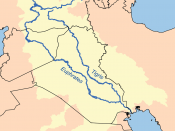
Iraq's total area is 271,128 square miles (just slightly more than twice the size of
Idaho). It's capital, Baghdad, is located at 33.20 north longitude, 44.24 east latitude. It's
boundaries are 2,222 miles long. With 906 miles bordering Iran, 83 miles bordering
Jordan, 149 miles bordering Kuwait, 502 miles bordering Saudi Arabia, 376 miles
bordering Turkey, and a coastline 36 miles long. The terrain in Iraq is mostly broad
plains, with reedy marshes in the southeast, mountains along toe borders with Iran and
Turkey.
The Climate in Iraq is most desert, with mild to cool winters and dry, hot
cloudless summers.
The northernmost regions along Iranian and Turkish borders
experience cold winters and occasional heavy snows. Iraq has few natural resources,
consisting of Crude oil, natural gas, various phosphates, and sulfur. Their maritime
(ocean) clams are just the continental shelf on their coastline, and twelve nautical miles
beyond that.
Iraq and Iran have just recently restored diplomatic relations in the year 1990, but
are still trying to work out written agreements settling their disputes from their eight-year
war concerning definite borders, prisoners-of-war, and freedom of navigation and
sovereignty over the Shatt-al-Arab waterway. In April of 1991, Iraq officially accepted
the UN Security Council's Resolution 687, which states that Iraq accepts the boundaries
that were set in it's 1963 agreement with Kuwait, and ending all claims to the Bubiyan
and Warbah Islands, and all claims to Kuwait. On June 17, 1992, the UN Security
council reaffirmed the finality of the Boundary...