The spleen is a soft, spongy organ of the lymphatic system. It serves two general functions in adults:
1.Fights infection. Acts as a giant lymph node, scanning erythrocytes, platelets and antigens. Lymphocytes produced in the spleen fight disease causing pathogens.
2. Filters aged erythrocytes, platelets and blood-borne antigens.
The spleen is the largest lymphatic mass in the body and lies intraperitoneally in the left upper quadrant. It sits on the left colic flexure1, in the left hyperchondriac region, between the stomach and diaphragm. Posteriorly, it is associated with the left 9th through 11th ribs, separated from them by the diaphragm. The diaphragmatic surface of the spleen is convexly curved to fit the concavity of the diaphragm. The posterior and inferior borders are rounded, whereas its anterior and superior borders are sharp and notched. The anterior aspect of the spleen contacts the posterior wall of the stomach and is connected to its curvature by the gastrosplenic ligament and to the kidney by the splenorenal ligament.
The spleen usually measures 12cm by 7cm, which is roughly the size of a clenched fist. It weighs around 180-250g.1, 2
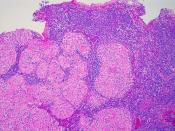
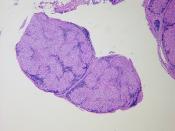
The spleen is entirely surrounded by a capsule of dense connective tissue which, in turn is covered by a serous membrane visceral peritoneum (except the hilus). The visceral peritoneum is a collagenous membrane made of bands consisting of collagen and reticular fibres that provide support for two main splenic parenchyma structures, the white pulp and the red pulp. Long protrusions called trabeculae of the capsule extend interiorly into the organ. The stroma of the spleen consists of the capsule and its protruding trabeculae, reticular fibres, and fibroblasts. The white pulp and red pulp of the spleen form the parenchyma of the spleen. 1, 2
The parenchyma of the spleen consisting of the white pulp...