Global Financing and Exchange Rate Mechanisms�
Global Financing and Exchange Rate Mechanisms
Joseph Rehman
April 19, 2010
University of Phoenix
MGT 488
Global Financing and Exchange Rate Mechanisms
Introduction
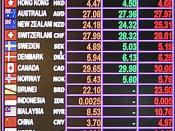
In this paper we will discuss hard and soft currencies. A currency is something that is exchanged for a good or a service. Most times this can be in the form of a paper bills and coins. The must have a monetary value, which that can either be a hard currency or a soft currency. According to the International Business textbook states that the Bank of International Settlement that $6.4 trillion is internationally financed by banks around the world and that the total world banking assets are over $20 trillion. These two different types of currency are very important to international trading which requires one of the two. Many times government who participate in any type of trade must keep careful track of their transactions and investments.
We will define how hard and soft currency and how they apply to the global financing and exchange rate mechanisms.
Hard currency is defined by Investopedia.com, "A currency, usually from a highly industrialized country, that is widely accepted around the world as a form of payment for goods and services. A hard currency is expected to remain relatively stable through a short period of time, and to be highly liquid in the forex market." Hard currency is one of the most valuable form when it comes to international trading. Hard currency mainly come from countries that have both political and economical stability, which are United States, Europe, Japan, and Australia. Some of the best examples of hard currency is the U.S. Dollar, the European Euro, the Japanese Yen, and the British Pound. Most the times hard currencies are backed up with a hard money...