Hello Everyone. I'm here to talk about the difference between prions, viruses, bacteria, protozoans, fungi and macro-parasites. These are all pathogens that cause diseases. I will also be giving examples of the diseases that these pathogens cause.
Prions are infectious agents which do not have a nucleic acid genome. Prion diseases are often called spongiform encephalopathies (mad cows disease) because of the post mortem appearance of the brain with large vacuoles in the cortex and cerebellum. Prion proteins are found in two forms, the wild type form (PrPc) and the mutant form (PrPsc). Once the protein that has been altered from its normal structure it can alter other proteins to form more prions. Examples of the diseases they cause are:
Scrapie in sheep
Chronic wasting disease in mule deer
Creutzfeld-Jacob disease in humans &
Alpers syndrome in humans
The 1st picture is of the difference between normal protein folding and prion protein folding.
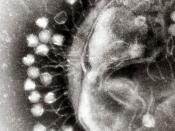
The 2nd picture is of a hamster prion.
Viruses are non-cellular (non-living) infectious agents consisting of a single type of nucleic acid (either RNA or DNA) surrounded by a protein coat. Some viruses have an additional layer around this coat called an envelope. Viruses are generally specific for a given host, although all organisms are susceptible to viral attack. There are thousands of different viruses that come in a variety of shapes. Many are polyhedral , or multi-sided. Other viruses are shaped like spiky ovals or bricks with rounded corners. Examples of the diseases they cause are:
Influenza
Measles
AIDS
Hepatitis &
Foot and mouth disease
The 1st picture is of the different structures. The 2nd picture is of the inside of a virus. The 3rd picture is of an actual virus.
Bacteria consist of only a single cell, with no internal membranes. Bacteria...
Nice work
nice work
3 out of 4 people found this comment useful.