IntroductionFor the past 27 years, Carroll's corporate social responsibility pyramid (CSR) has been widely used by top management and journals to better define and explore CSR. The different components in the pyramid help managers see the different types of obligations that society expects of businesses. It is easily understandable and simple. However, the new challenges faced by corporations in the 21st century have warranted a re-examination of Carroll's pyramid.
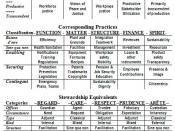
Carroll's CSR PyramidCarroll's four part CSR pyramid depicts the economic, legal, ethical and discretionary responsibilities that society expects of organizations. Carroll has integrated concepts of stakeholders and corporate citizenship into his pyramid.
The base of the pyramid is economic responsibility and it gives top priority to economic performance. A business has to be profitable; maximising profits, minimizing costs, plan for the future and provide shareholders with sufficient and attractive returns. The stakeholders affected most in this group are its employees and shareholders.
The legal responsibility is second in the hierarchy. Businesses are expected to pursue profits within the framework of the law. Society expects businesses to adhere to all regulations and laws, honour its contracts, warranties and guarantees.
Third is ethical responsibility and it involves avoiding questionable practices. It includes all activities which have not been anticipated or legislated by society. Organizations must accept emerging values and norms of society. Businesses are to operate above mere compliance of the law. Ethical responsibilities are more difficult to deal with as they tend to be new, ill-defined or continually under public debate.
At the top of the pyramid is philanthropic responsibility. It involves giving back to the community and being a good corporate citizen through donations and active participation in charities or other community welfare programs. Such responsibility is desired but may not be necessarily performed and hence is separate...